Overview
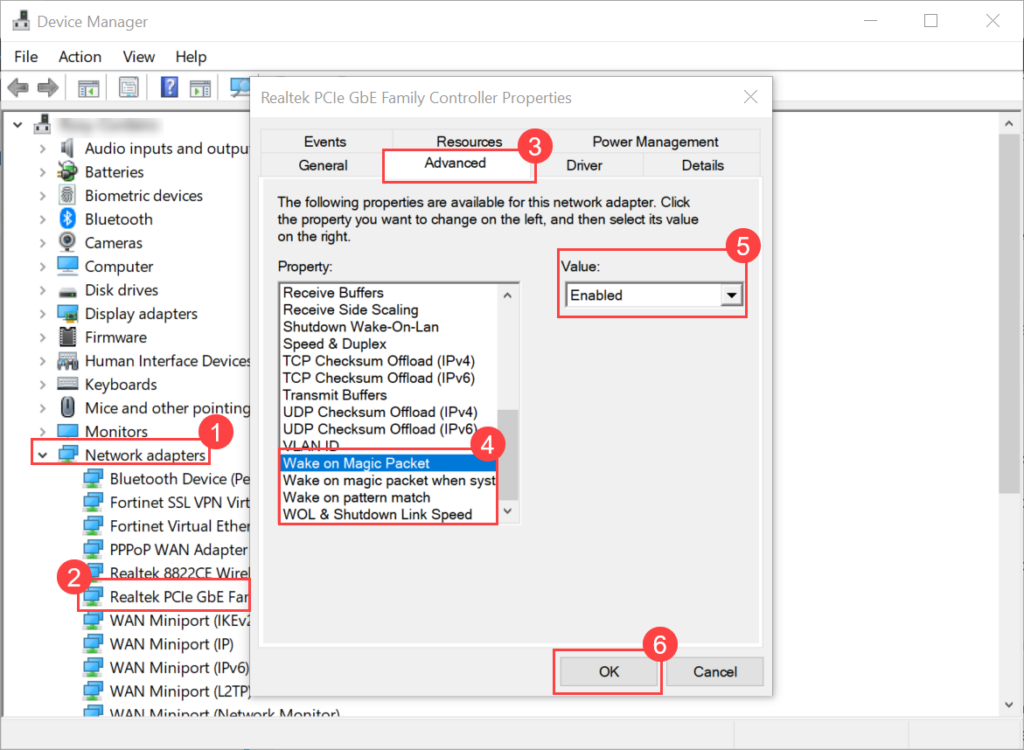
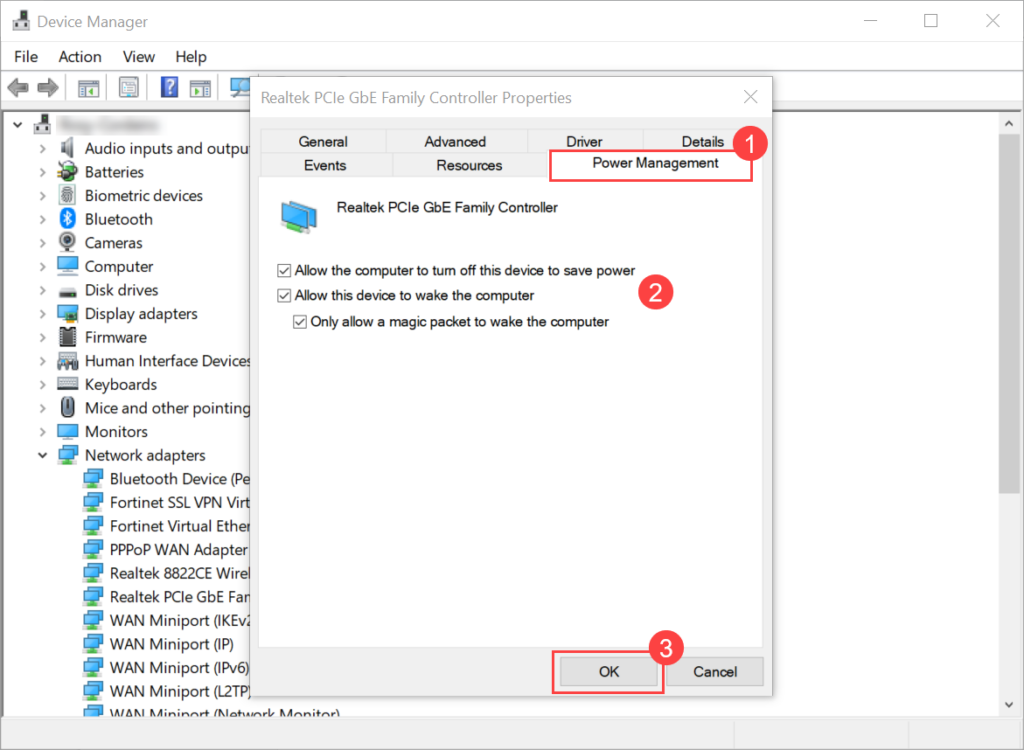
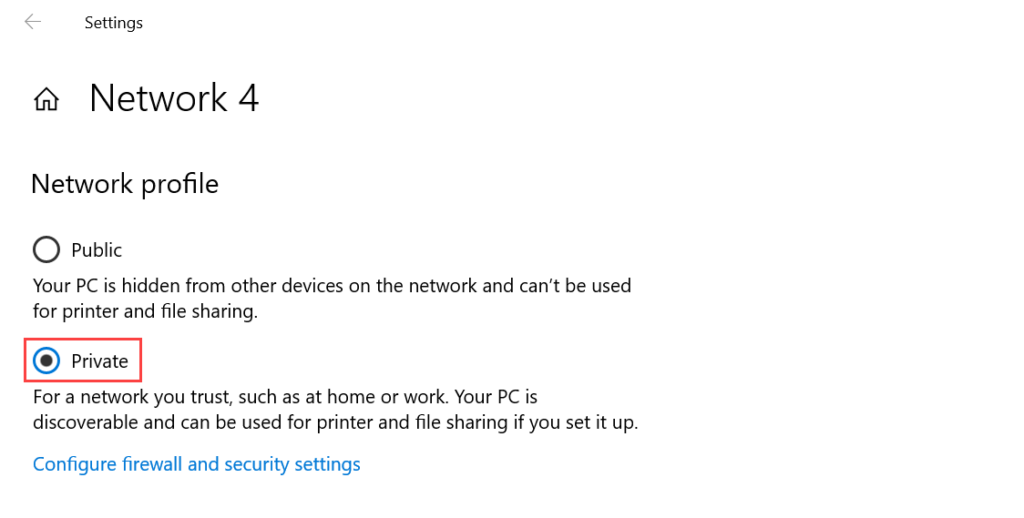
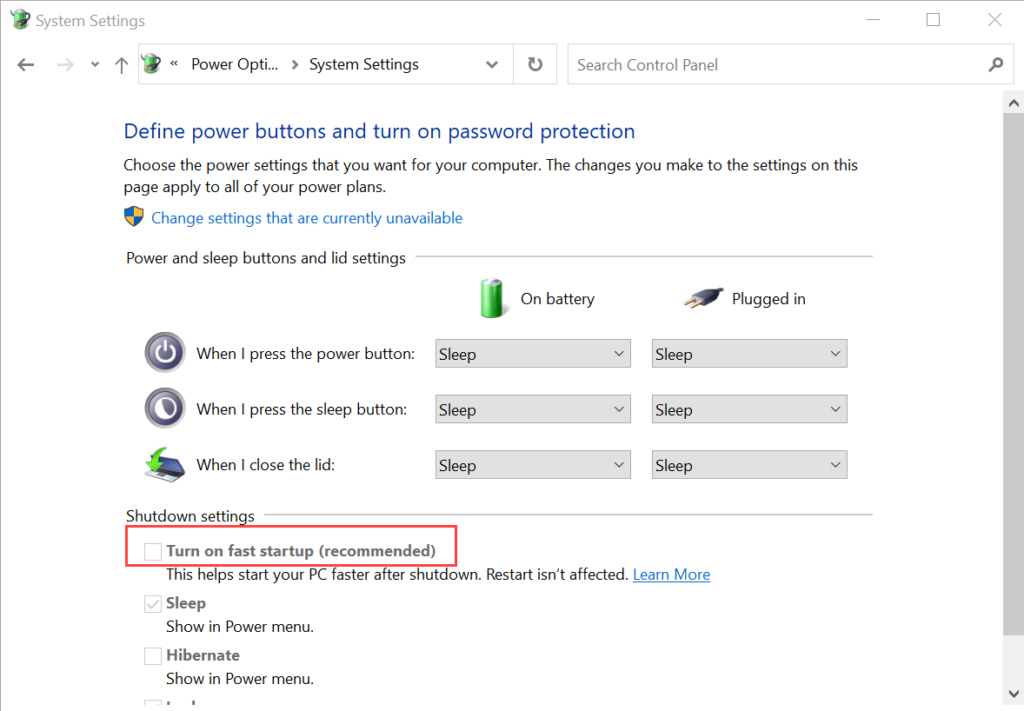
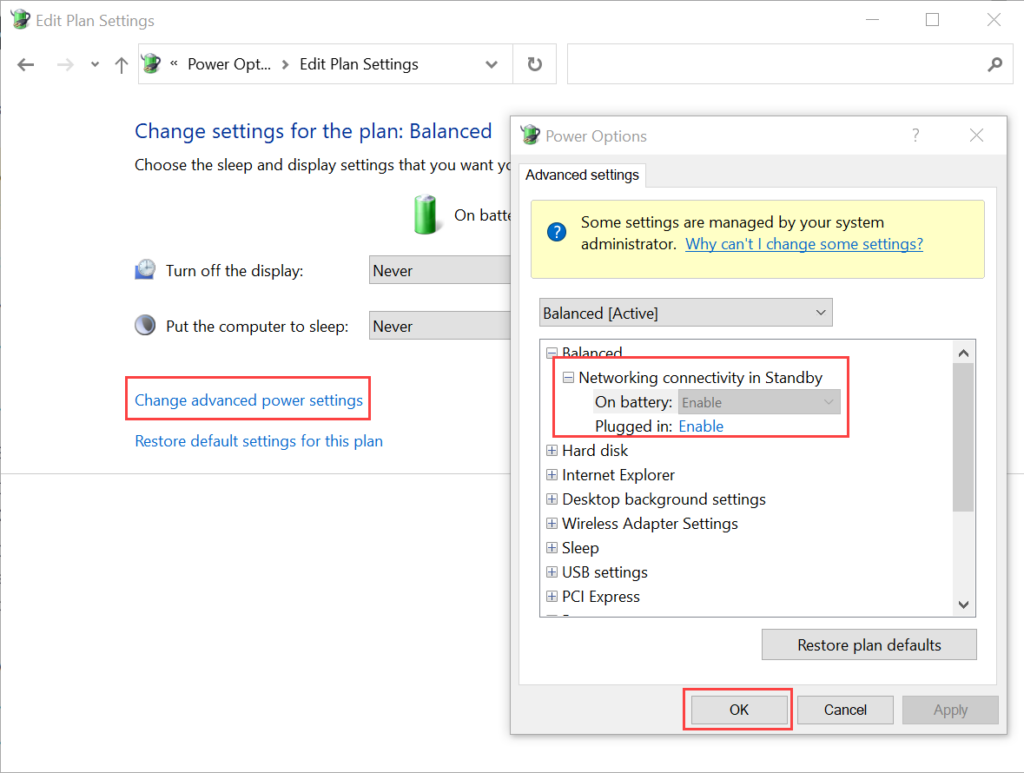
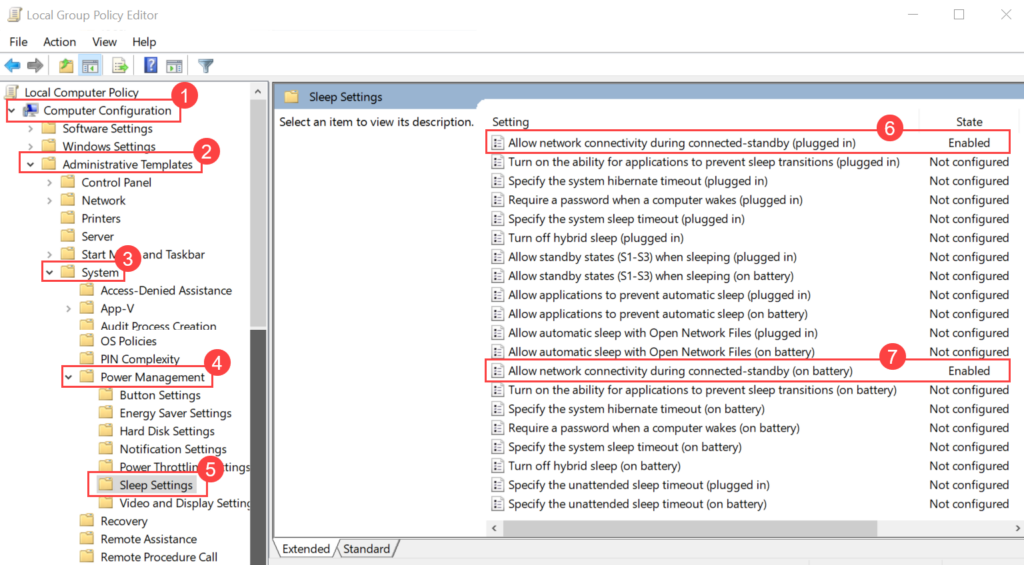
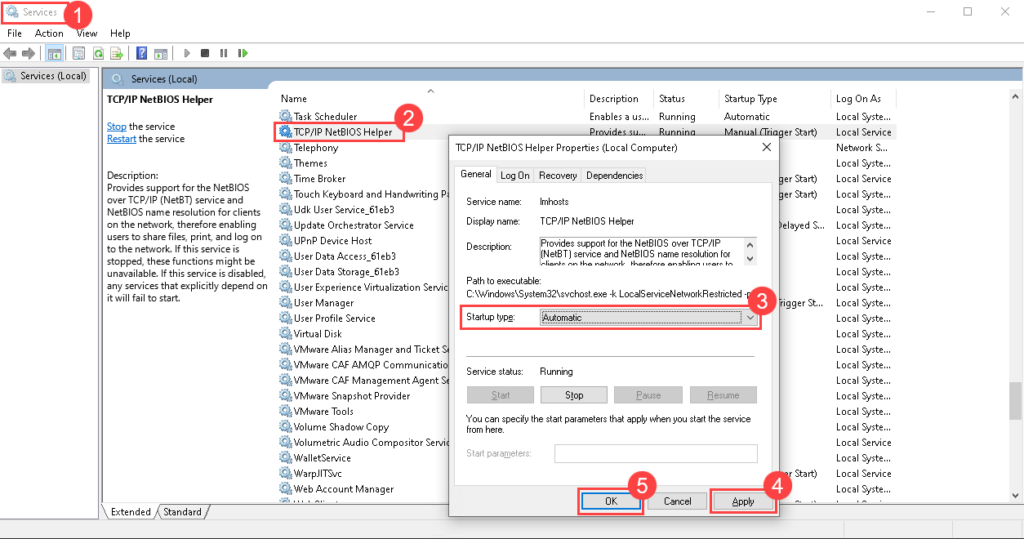
Wake On LAN (WOL) is an Ethernet computer networking standard that enables you to awake or start a computer remotely from anywhere. It wakes up the target computer by sending a network message. A computer that has the Internet connection and is Advanced Configuration Power Interface (ACPI) compliant can be turned on remotely. It requires a special software program like Motadata ServiceOps that sends a wake up signal to another computer in the same LAN. It is also possible to initiate the message from another network by using subnet directed broadcasts.
With WOL configured, you need not to go personally and turn on the system for performing some task. You can simply sit at one place and through ServiceOps initiate the WOL process either manually or automatically using a scheduler.