Change Management
Once the root cause of the problem is found, and a change is required as a solution, the change management module comes into picture.
What is Change Management?
Change management is an approach with standard methods to process the changes in the IT infrastructure. It includes planning and a workflow to minimize the negative impact during and after the change is processed. The change management ensures efficient and prompt response to requests or problems. It maintains an equilibrium between the expected outcome and possible failures.
What is a Change Request?
The change, as the name indicates is the new difference required to be processed from the agreed existing requirements. For example: An employee can request a change of Laptop. A change request has a life cycle and uses planning and workflow to process a change request.
Change Management in ServiceOps
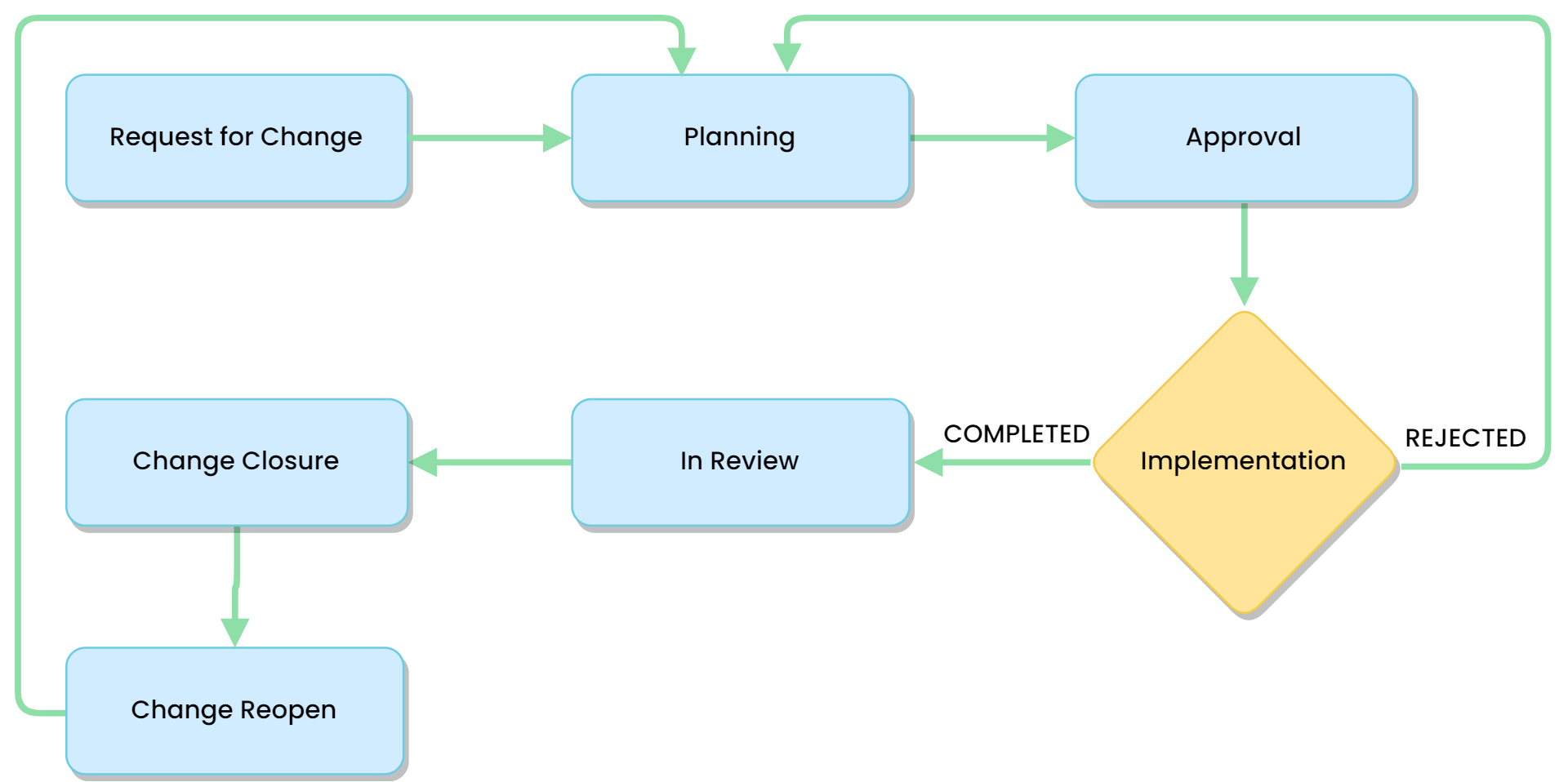
Whenever a change request is created with respect to an incident or problem, its resolution is planned, approved from the approvers, implemented, reviewed, and lastly closed.
The ServiceOps Change Management involves the following activities: