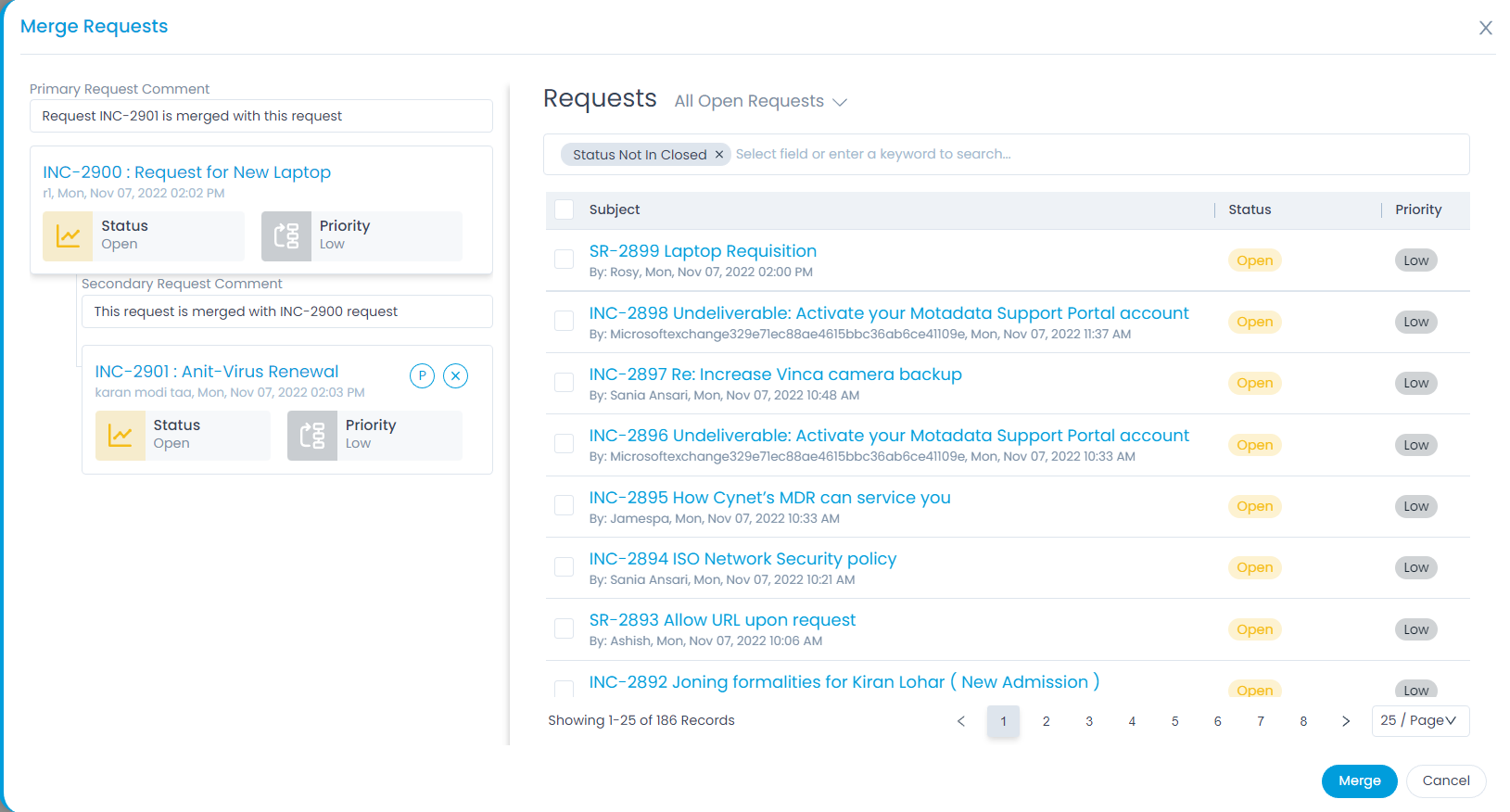
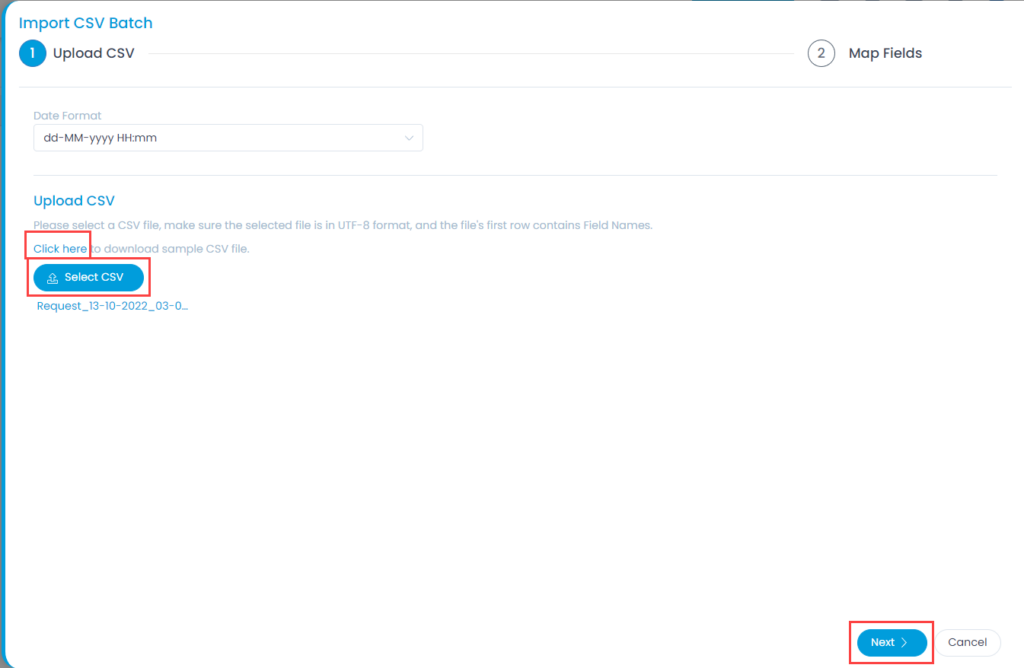
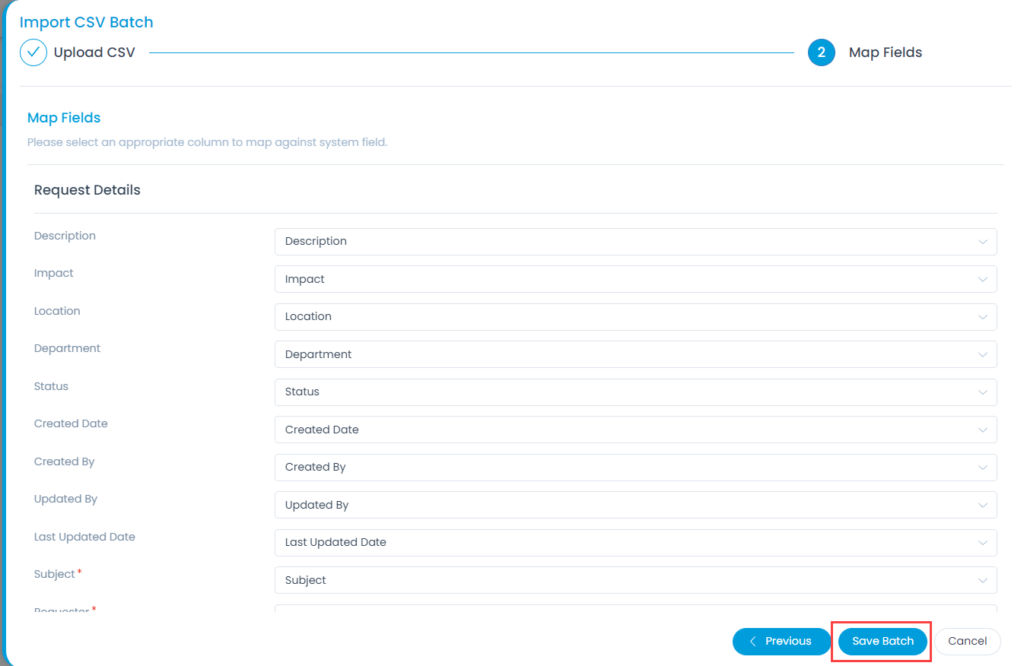
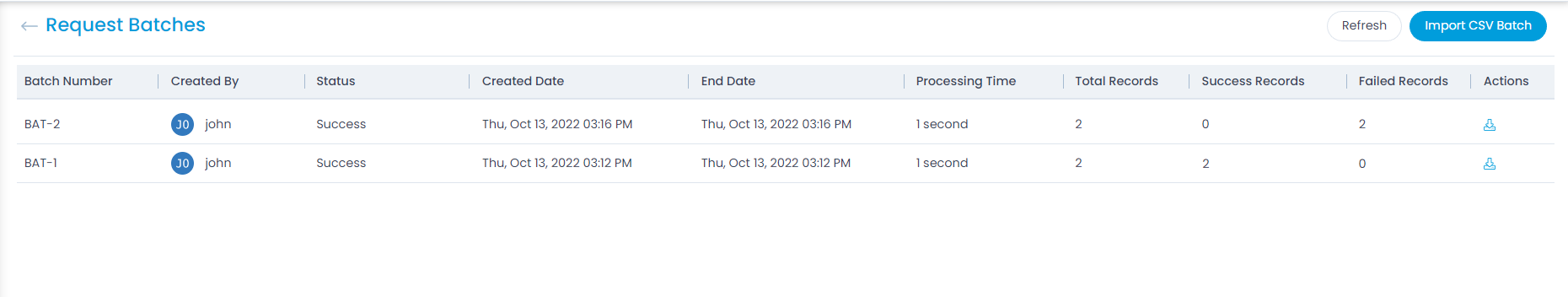
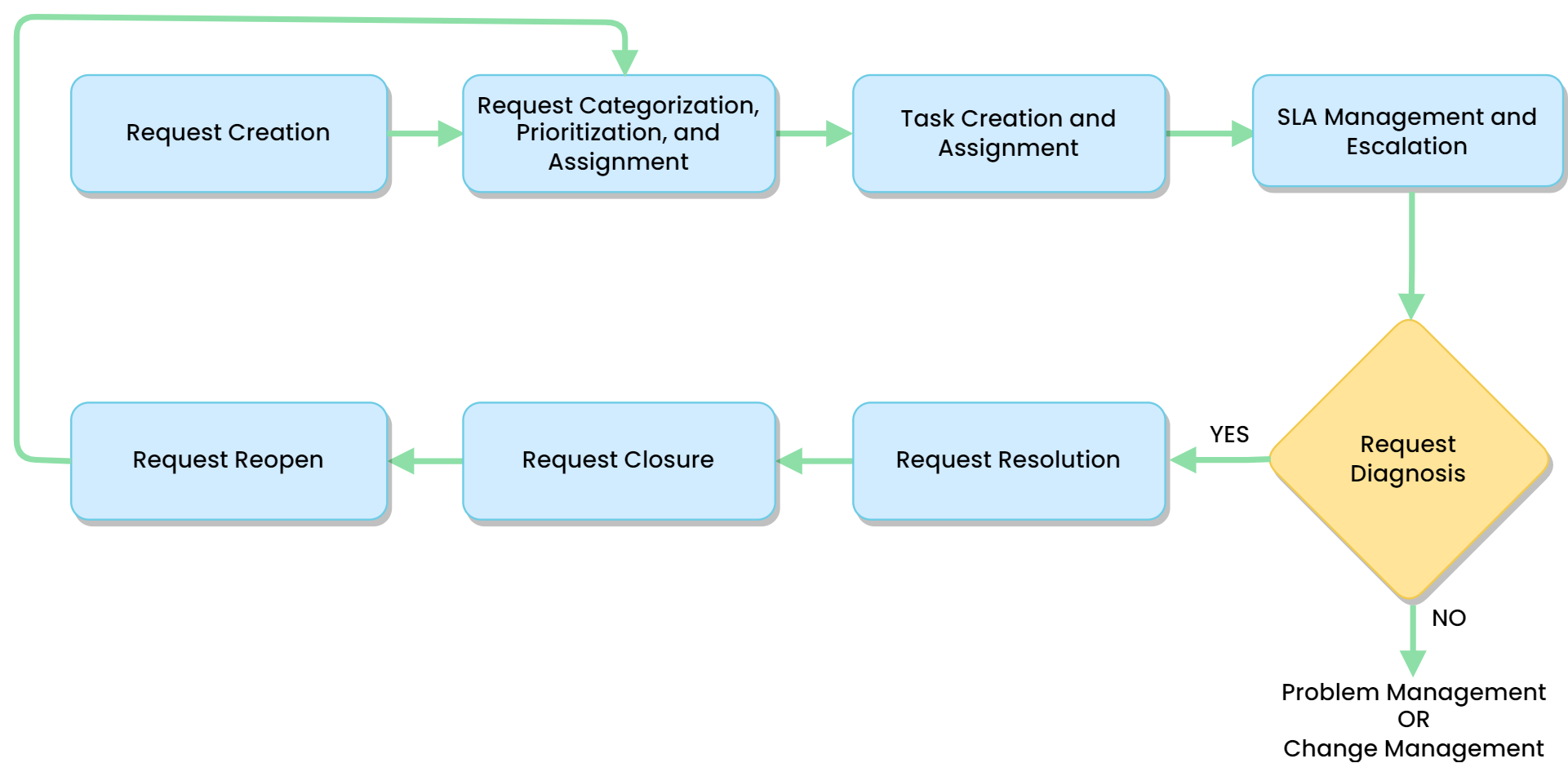
Mark Requests as Spam
This option enables you to mark the irrelevant requests as spam requests. Once you mark the request as spam, the system adds a ‘Spam’ tag to the request, and it disappears from the request list.
Irrelevant and unsolicited messages sent are Spam; here the messages are in the form of tickets (Requests). It may happen that some Requests you receive are irrelevant, and you want them to disappear. You can discard a Request as a Spam, and it disappears from the main server.
Mark Spam from List Page
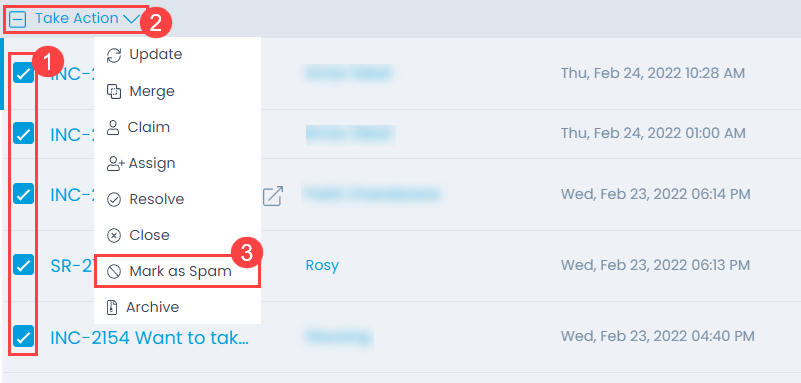
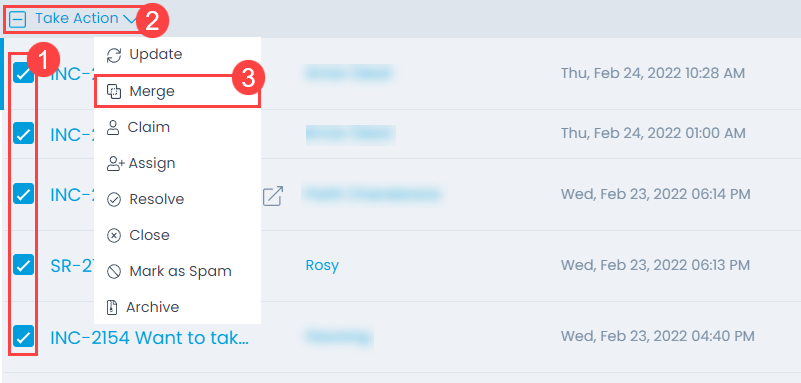
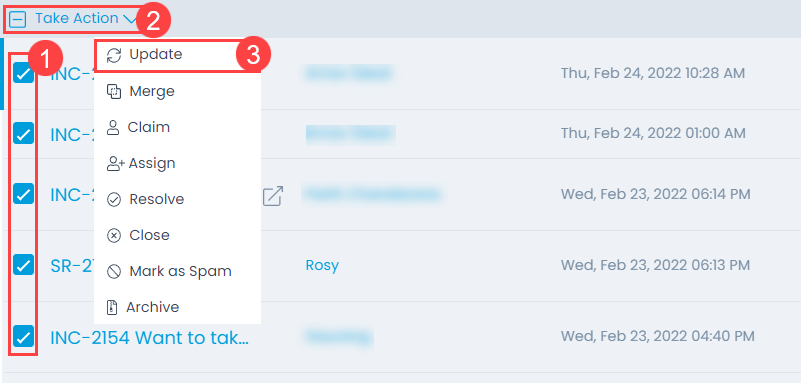
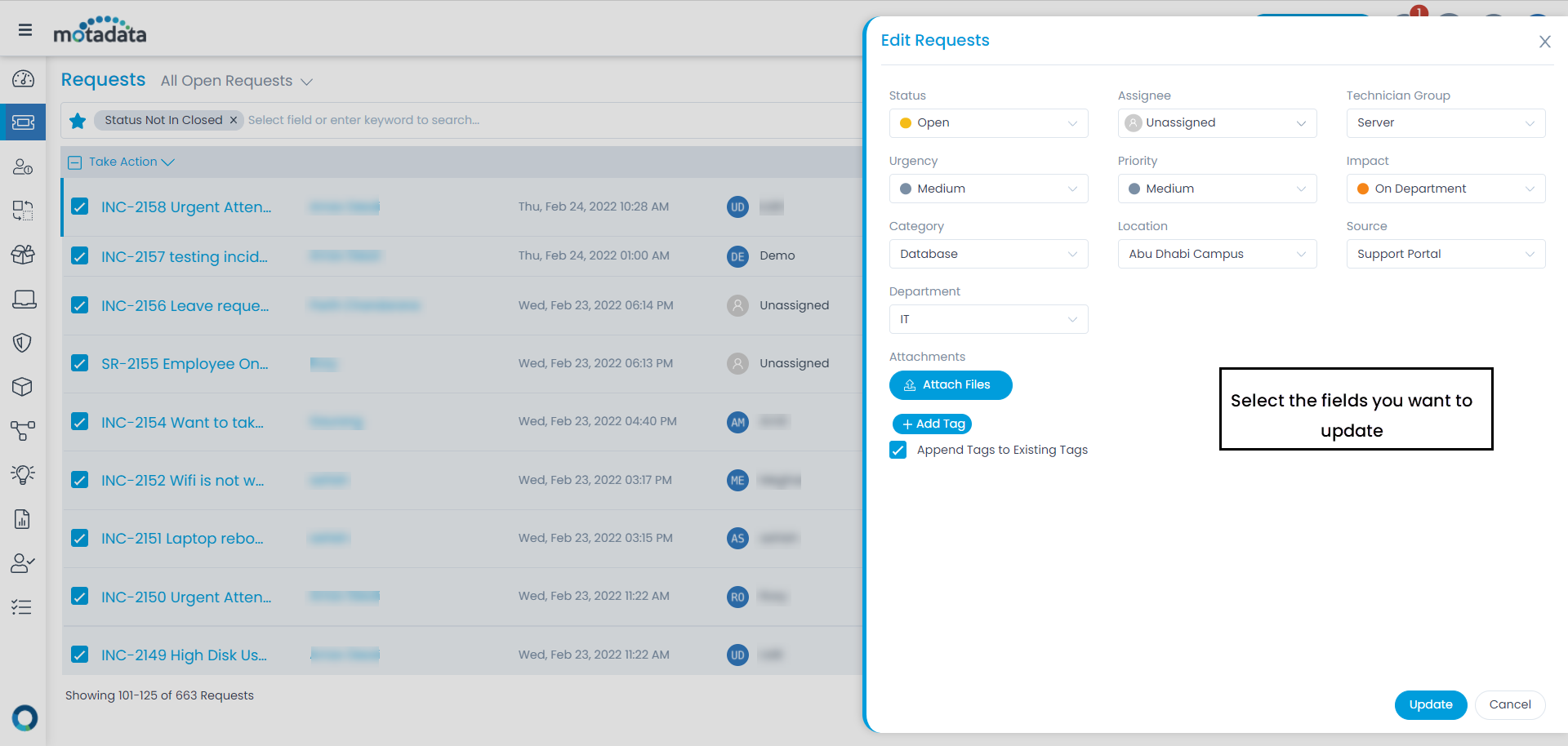
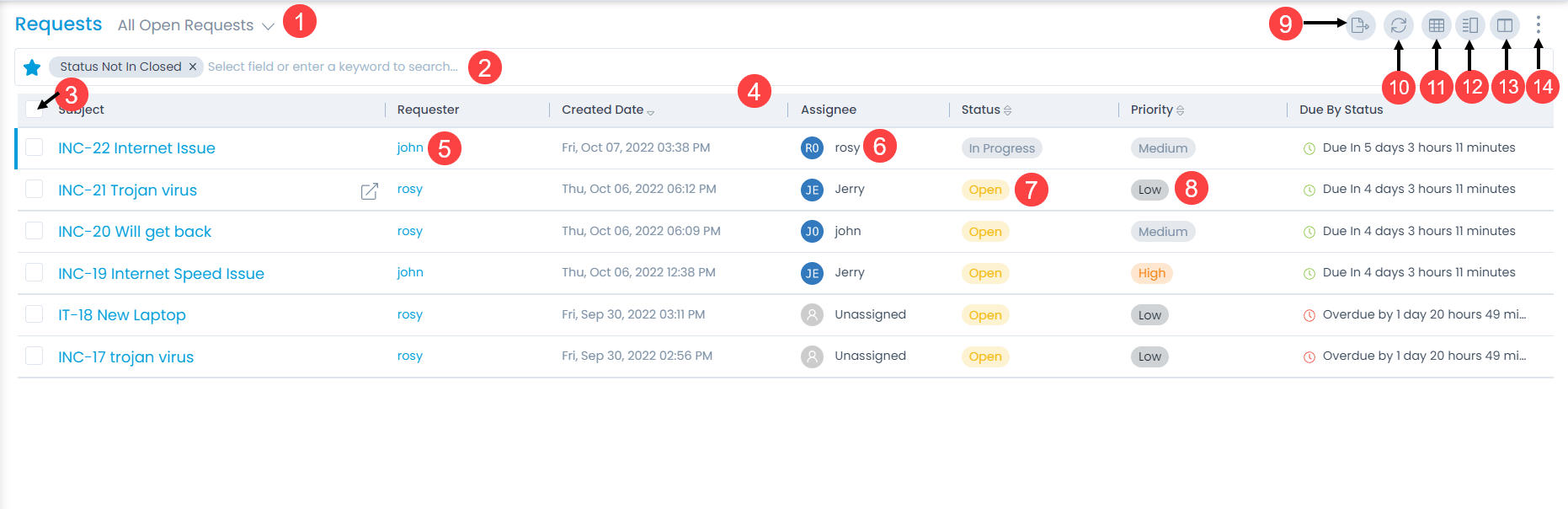
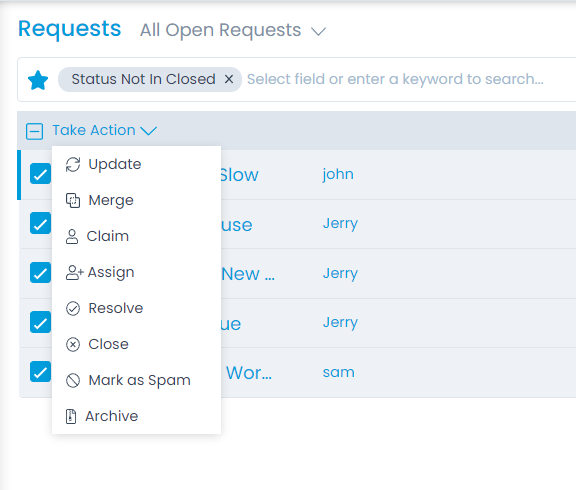
To mark the request as Spam, select the desired tickets, click the Take Action dropdown, and select Mark as Spam option as shown below.
Once the option is clicked, a confirmation message will appear. Click Yes to confirm the action.
Mark Spam from Details Page
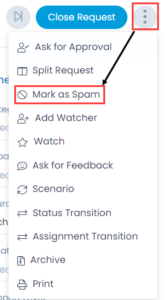
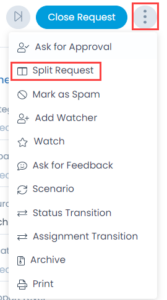
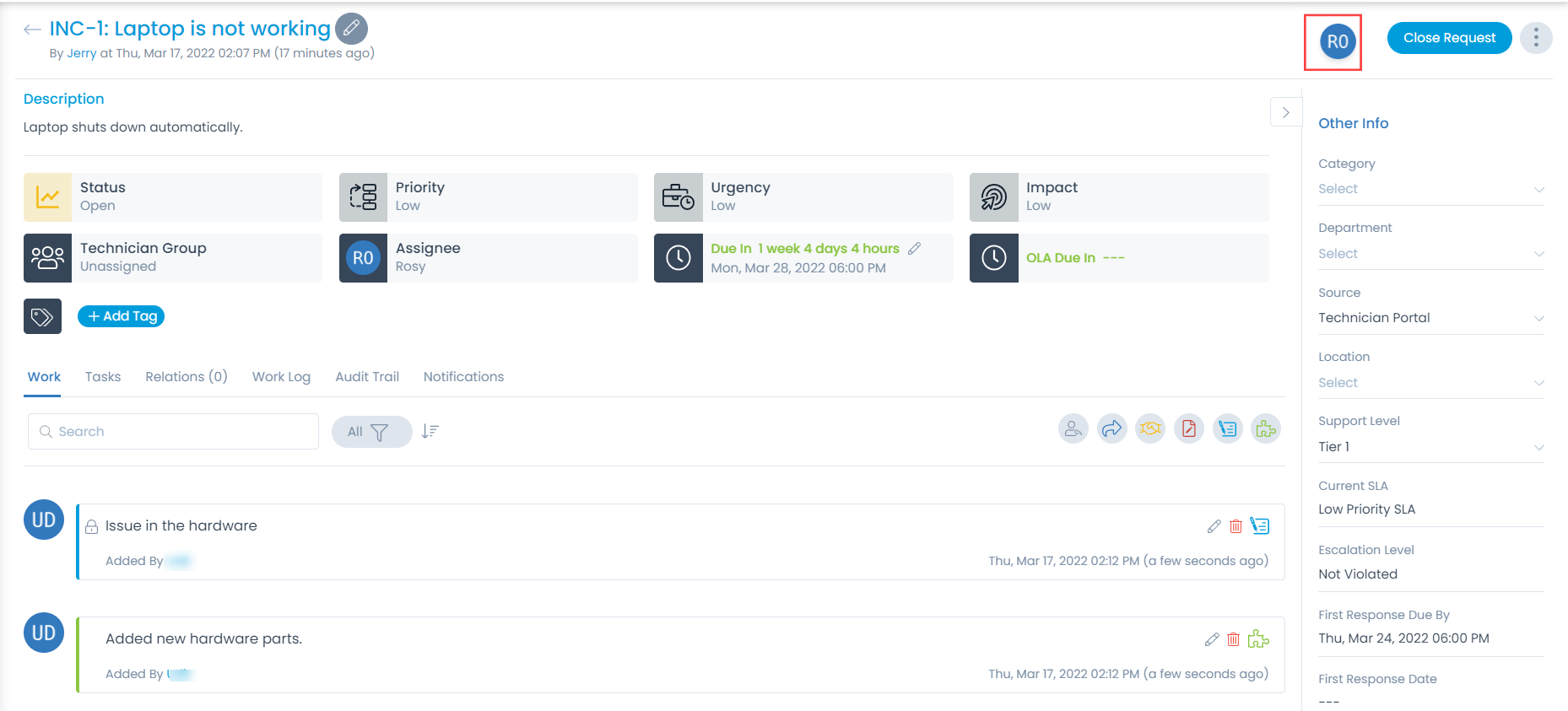
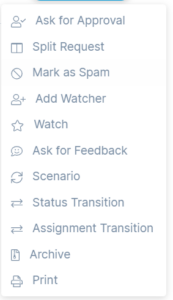
On Request Details page, click on the 3 vertical dots at the top-right corner of the screen, and select Mark as Spam from the dropdown.
Once the option is clicked, a confirmation message will appear. Click Yes to confirm the action.
View Spam Requests
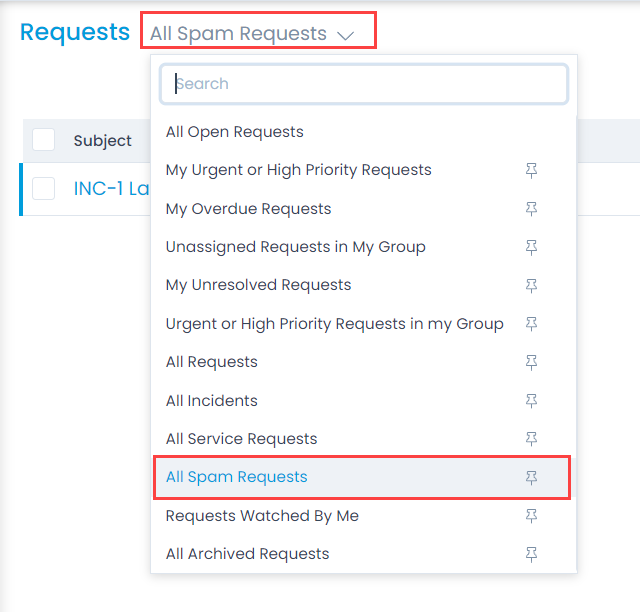
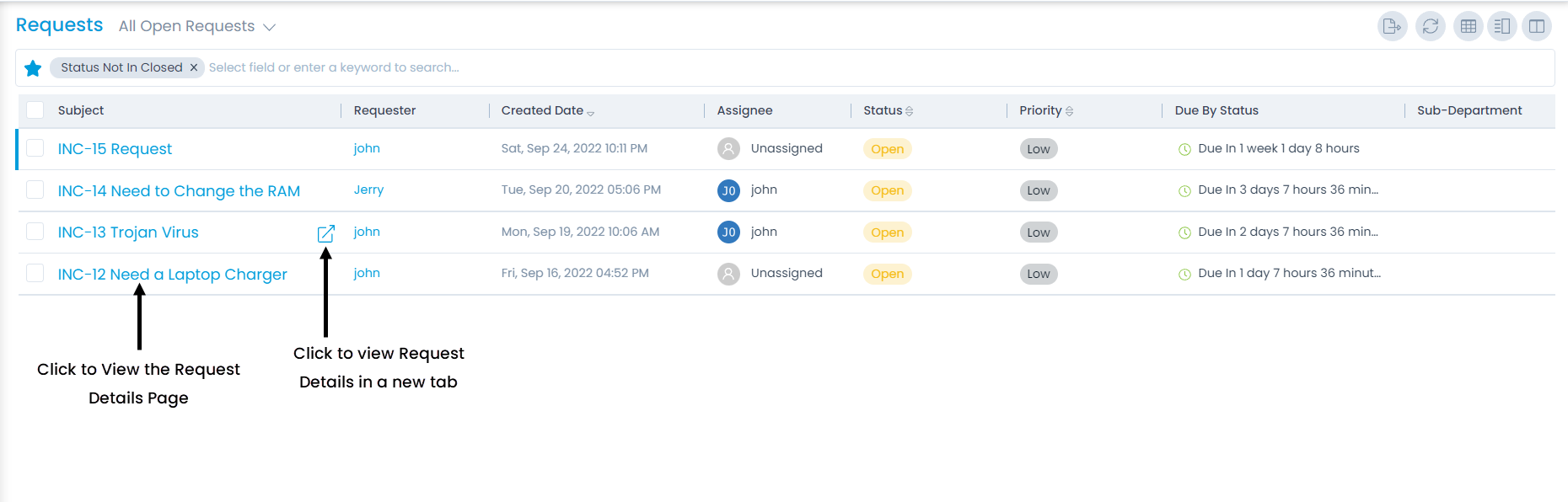
You can view the requests that are marked as spam from pre-defined search criteria. At the top of the list page, select the criteria: All Spam Requests as shown below.
Unmark As Spam
This option enabled you to move the requests from Spam to the normal request list. There are two methods to do this:
Option 1: Unmark from List Page:
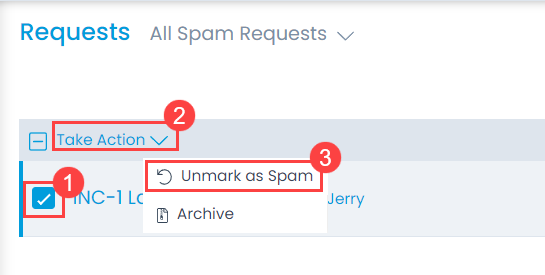
To unmark the request from the spam list, select the records, click the Take Action dropdown, and select the Unmark as Spam option as shown below.
Once the option is clicked, a confirmation message will appear. Click Yes to confirm the action or No to discard the changes.
Option 2: Unmark from Details Page:
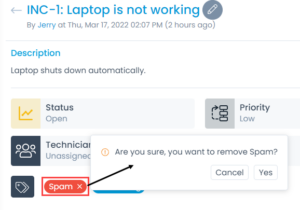
On the Request Details page, you can unmark the spam by deleting the spam tag. System will ask you to confirm deleting the spam tag as shown below.
Archive Spam Request
Archiving the spam request moves the request from spam list to the archive list. To archive the request, refer to the Archive Requests page.