Advantages of a Network Management System
NMS is a broad family of computer software that supports networking devices such as routers, switches, access points, and remote controls. NMS systems are also known as network controllers because they are typically used to manage networks and other aspects of the network.
A Network Management System (NMS) offers several advantages that greatly benefit network administrators and organizations. Here are some key advantages of implementing an NMS:
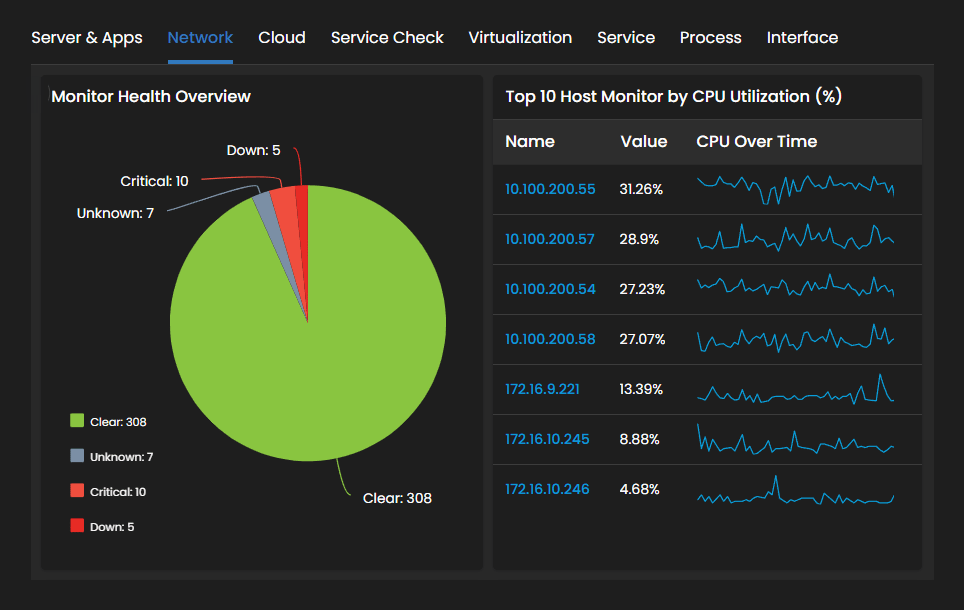
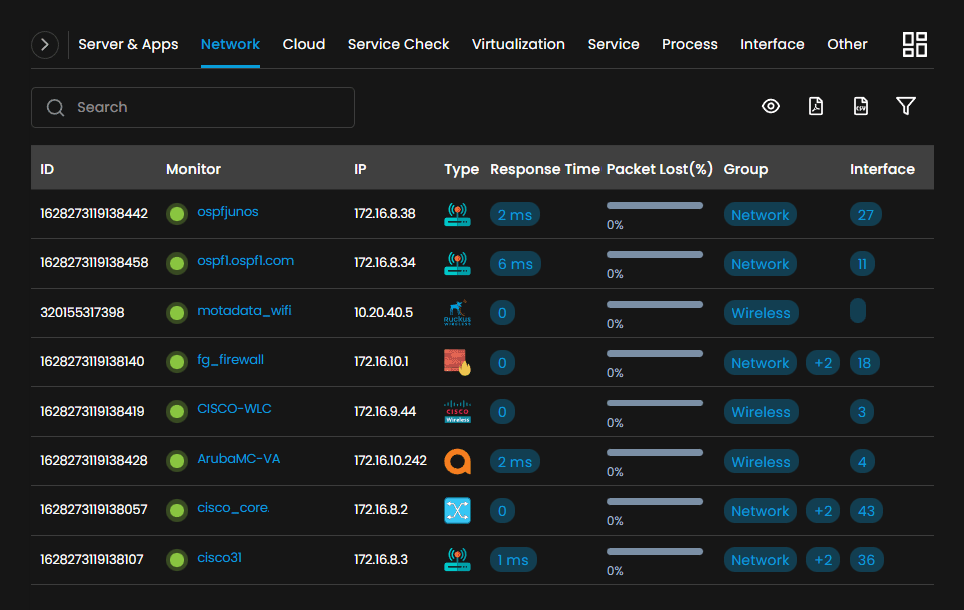
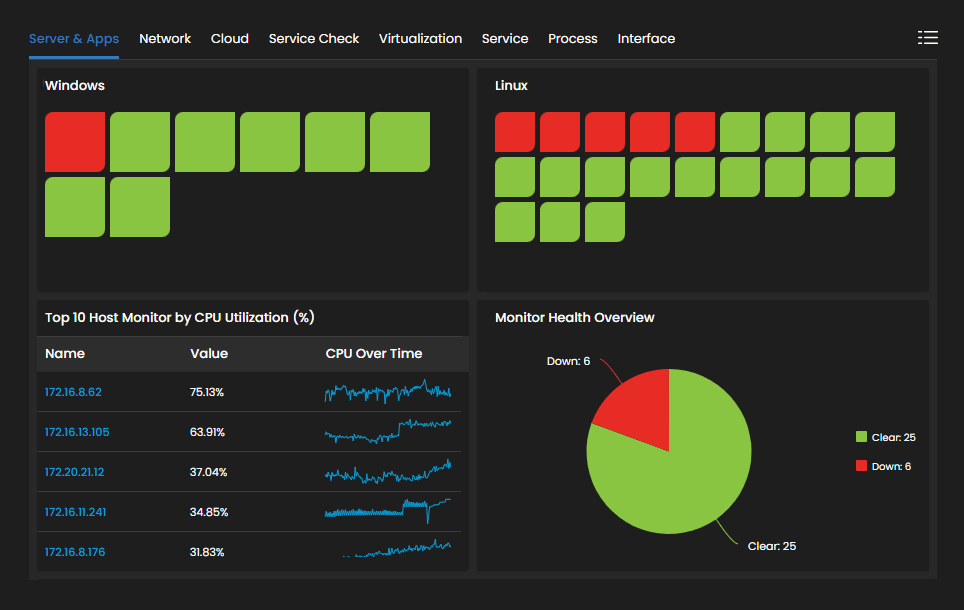
Centralized Network Control: An NMS provides a centralized platform for managing and monitoring network devices, configurations, and services. It offers a unified view of the entire network infrastructure, allowing administrators to control and troubleshoot network components from a single interface efficiently.
Proactive Issue Detection: NMS tools continuously monitor network devices, interfaces, and services, enabling proactive detection of network issues. Real-time alerts and notifications notify administrators about potential faults, performance degradation, or security threats, allowing them to address problems before they escalate and impact network operations.
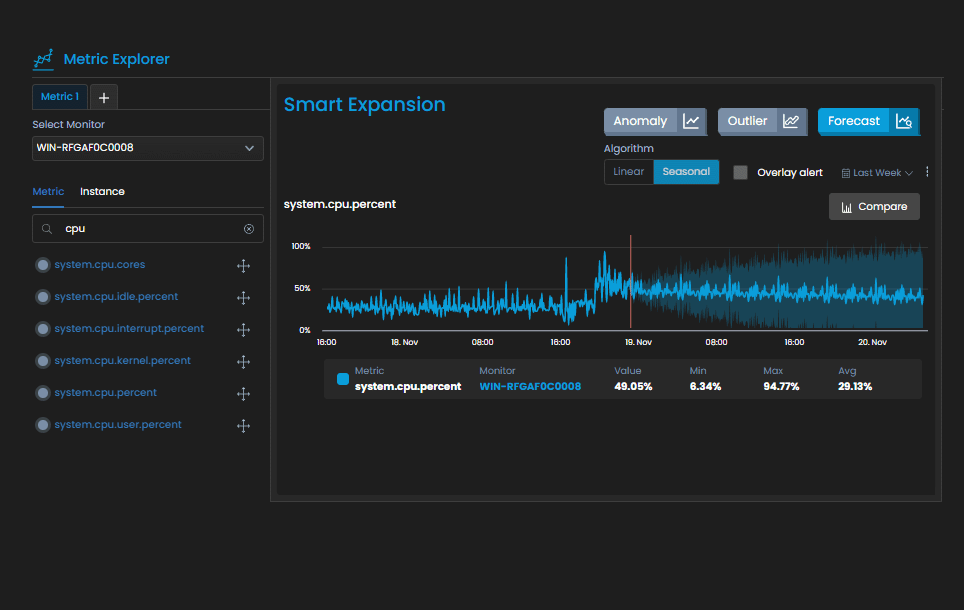
Improved Network Performance: By monitoring network performance metrics such as bandwidth utilization, latency, and response times, an NMS helps administrators optimize network performance. They can identify bottlenecks, plan for capacity upgrades, ensure efficient resource allocation, enhance network performance and user experience.
Efficient Troubleshooting: NMS tools provide detailed insights into network issues, making troubleshooting faster and more effective. Administrators can analyze historical data, track performance trends, and correlate events to identify the root cause of problems. This accelerates the resolution process and minimizes network downtime.
Enhanced Security: NMS systems play a crucial role in network security management. They monitor and detect security breaches, unauthorized access attempts, and abnormal network traffic patterns. Administrators can implement robust security measures, enforce access controls, and respond promptly to security incidents, improving the overall network security posture.
Streamlined Configuration Management: NMS tools simplify the management of network device configurations. They enable administrators to centrally deploy and update configurations, enforce consistency, and ensure compliance with network standards. This reduces configuration errors, improves network stability, and simplifies administrative tasks.
Effective Resource Planning: NMS tools provide valuable insights into network usage, capacity trends, and performance statistics. Administrators can use this information for effective resource planning, such as identifying underutilized or overutilized network segments, optimizing network bandwidth, and planning for future network expansion or upgrades.
Reporting and Analysis: NMS tools offer reporting capabilities, allowing administrators to generate performance reports, trend analysis, and usage statistics. These reports aid in decision-making, capacity planning, and network optimization. They also provide valuable information for audits, compliance assessments, and performance evaluations.
Implementing an NMS offers centralized control, proactive issue detection, improved performance, efficient troubleshooting, enhanced security, streamlined configuration management, effective resource planning, and valuable reporting and analysis capabilities. These advantages contribute to a stable, secure, and optimized network infrastructure, increasing operational efficiency and better user experiences.