Each software performs and responds differently in dynamic and distributed networks. In fact, as more and more technologies are developing, it is becoming difficult and challenging for businesses to understand the needs and concepts.
Hence, it has become essential to get a better understanding of how the software performs in real-world scenarios and tracks all the advancements made on several products.
There is a clear demand for a simple method for developers to collect data from these different products and share it for monitoring and analysis.
The actionable insights can be later used for making informed decisions. That’s the underlying reason behind the creation of telemetry.
Telemetry is a process that helps organizations and industrial experts collect data from different systems, store it, and analyze it for better performance delivery and informed decision-making.
This practice, which involves monitoring and analysis, spans across various sectors such as medicine, transportation, and others and is not limited to only the corporate world.
Let us learn about telemetry monitoring, how it works, its benefits, use cases, and challenges. Further, we will pen down some of the best practices that will help your organization in smooth operations and informed decisions.
What is Telemetry?
Telemetry is a system or a process that allows IT teams to collect, record, and transmit data automatically from remote and other sources for monitoring and quick analysis.
The collected data may include information related to radio signals, cables, or GSM, based on the application. In addition to software development, telemetry is also used in other fields as well, for example, medicine and meteorology.
In the IT environment, professionals mostly use the telemetry data to gain detailed insights into the performance of a system and areas that require immediate attention.
Basically, the implementation of this practice has made it easier for software developers to create better applications and improve customer experience.
How does Telemetry work?
Here are a few steps that will help organizations gain great benefits from telemetry data:
1. Identify telemetry requirements
Firstly, it is essential to understand and identify what information you want to track with the help of telemetry. For example, in the IT infrastructure, you might want to keep track of computers, networks, servers, and IT staff.
Basically, you need to identify the metrics you will be using and how you’re going to do data collection.
2. Configure telemetry instrumentation
Secondly, a telemetry connection must be established between the data-sending system and another system. For example, if you want to track or collect the application data, the application must provide details covering all the specific events, including when a user registers in or takes an action.
Also, if you use a queue system to transfer data, you will need to configure the transmission of data and reception channels. Additionally, in this stage, it also checks for the accuracy and safety before sending the data.
3. Transmit the telemetry
In this stage, the telemetry data must be sent to the other system in real-time using different protocols or techniques. The mode or method of transmission may vary as per the data type.
4. Storing all the telemetry data
You must store all the data in a central database system for real-time analysis. Later, you can use this large amount of data stored in a data lake for historical analysis as well.
The benefit of a centralized database is it helps in better application performance monitoring, tracking trends, patterns as well as anomalies in real time.
5. Analysis and Visualization
There are several analysis tools that are used by teams after the data is collected and stored in the telemetry storage.
With the help of these insights, it becomes easier to identify and fix errors, resulting in delivering a better user experience and informed decision-making.
Why is Telemetry Important?
Many businesses and industries use this monitoring tool for it offers several benefits. Here are some of the main reasons it is becoming important in today’s time:
Better Decision Making – With the helpful insights gathered from the telemetry data, organizations can quickly identify and resolve issues, resulting in informed decisions and overall system stability.
Improved Performance – By having a clear visibility into the system, processes, and performance of applications, users can work on the areas of improvement in real-time and optimize operations, resulting in better performance delivery and efficiency.
Enhanced customer experience – Another reason it has become crucial is it helps identify and understand unique customer needs and requirements. By analyzing customer data, users get an idea of the preferences of a customer and accordingly optimize products and services to meet those needs and satisfy their customers.
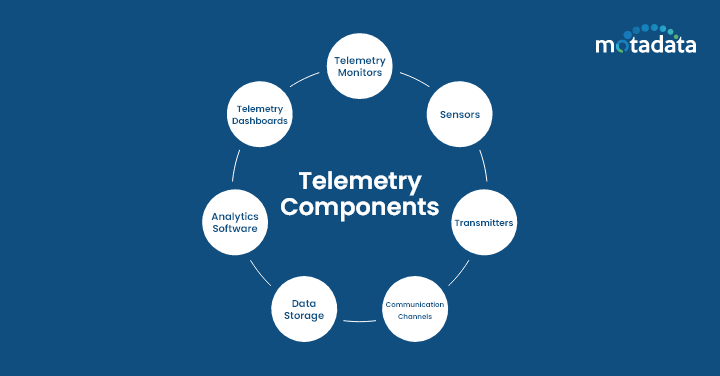
Telemetry components
Telemetry systems comprise different components that collaborate to gather, send, and process data, including:
- Telemetry monitors – These record and forward data from sensors or electronic devices.
- Sensors – These are used for taking physical measurements and turned into electrical signals using telemeter.
- Transmitters – Responsible for encoding and sending data across communication channels.
- Communication Channels – The wired or wireless medium through which data is sent to the other system
- Data Storage – A centralized database where all the information collected is stored for future analysis
- Analytics Software – A software used to identify unusual patterns and gain other helpful insights for better decision-making
- Telemetry Dashboards – These dashboards help display all your telemetry data in better form like charts and graphs for better understanding.
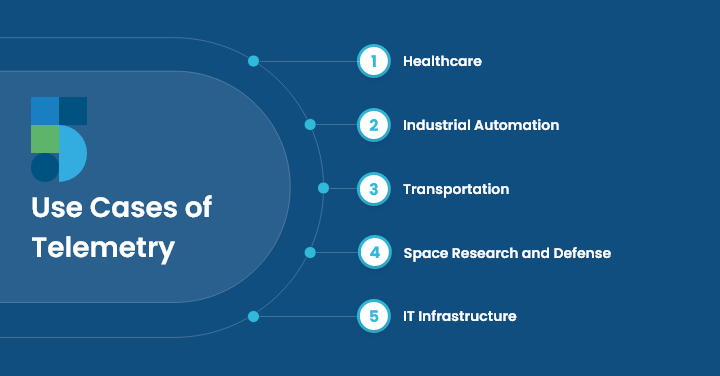
Use Cases of Telemetry
Professionals from various industries and sectors use telemetry, including:
Healthcare – With this monitoring tool, healthcare authorities can track the heart rate, health of patients, telemedicine applications, and more.
Industrial Automation – Manufacturing industrialists and professionals can also monitor and control all the processes and performance of equipment using telemetry monitoring.
Transportation – Be it vehicle performance monitoring or fleet management, professionals can use telemetry for better efficiency and safety.
Space Research and Defense – Astronomers, spacecraft, and airplanes are tracked, operated, and maintained via telemetry by NASA and the U.S. military.
IT Infrastructure – With this monitoring tool, businesses can keep track of network components, servers, applications, and IT staff in real time.
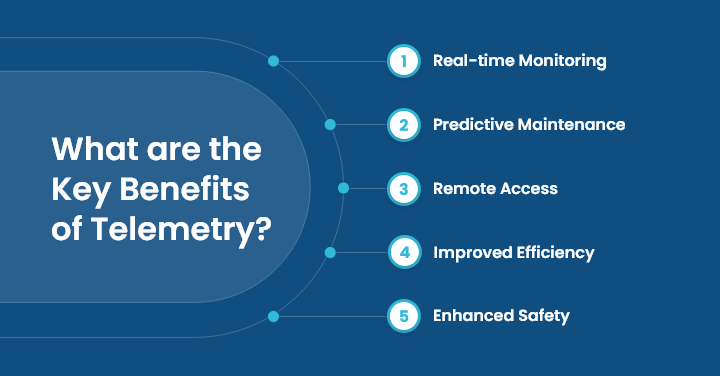
What are the Key Benefits of Telemetry?
Here are some of the major benefits of telemetry, including:
1. Real-time Monitoring
With the help of this monitoring practice, businesses can keep better track of UX as well as application performance in real time. It provides detailed insights into the features, user engagement, device configurations, and database errors.
By having a good knowledge of faults and weak spots in an application developers can fix system issues and improve performance.
2. Predictive Maintenance
Telemetry helps identify issues at an initial stage and predict systems that might fail in the coming period with constant monitoring. These insights further aid in quick troubleshooting and downtime reduction.
3. Remote Access
It allows users to keep watch over system resources and performance from a remote location, thus reducing the need for on-site visits and saving time.
4. Improved Efficiency
With real-time detection of faults and errors in a system, businesses can save on additional maintenance expenses, better optimize resources, and improve performance.
5. Enhanced Safety
With telemetry monitoring, users can even identify and pinpoint threats at an early stage and reduce the risk of accidents, resulting in a safe environment for both employees and customers.
Drawbacks and Challenges of Telemetry
No doubt telemetry comes with various benefits but it is also challenging at times. Here are the following challenges that most users face with telemetry systems:
Data access
The quality of telemetry relies on the amount of data the system can collect. For privacy-related concerns, end users may disable telemetry, which reduces the number of users who can provide data.
Data deluge
More IoT devices are collecting telemetry data than ever before, which has caused systems to produce more data than analysts can process.
Legacy issues
Telemetry may not always work with older apps and devices. Technology such as Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) offers an alternative for network monitoring. If the equipment is older and does not support telemetry, SNMP functions better.
Types of Telemetry
DevOps and software developers can use several IT monitoring tools available in the market to measure telemetry in software development.
Here are the different types of telemetry data that can be monitored with the help of these tools:
Metrics Telemetry – Be it server metrics, processor use, CPU usage, physical memory, response time, or any other data that is measured over time are collected using this type.
Logs Monitoring – This type of telemetry includes log files or time stamped text records that include all the information related to a system at a specific period.
Application Telemetry – This type of data includes all the activities related to application monitoring, i.e., application deployments, security breach, response rate, etc.
Traces Telemetry – An application’s activities are represented by a trace, which is a group of hierarchically connected spans.
Network Monitoring – It collects all the information related to network performance, i.e., switches, bandwidth, and other network components.
User Telemetry – When a user interacts with a product —for example, clicks a button, views a certain page, or comes across a specific error page—user telemetry gathers data.
Cloud Monitoring – This type helps monitor cloud availability, latency, hybrid cloud usage, and other metrics
How Is Telemetry Data Measured?
All you need to do is monitor Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and other system metrics to measure telemetry data. By doing so, users will gain detailed insights into the metrics, including network traffic insights, bandwidth usage, server performance, and other information crucial for smooth business operations.
In this process, sensors collect all the information and later store and use it for root cause analysis.
Organizations with large-scale repositories often store this gathered information for historical analysis, trend analysis, and anomaly detection.
With this information, administrators can get a quick insight into user behavior, application performance, and other parameters that help in faster troubleshooting and informed decision-making.
Why Is Telemetry Important for IT Observability?
With telemetry, developers can get better visibility into the user behavior, performance, and other potential problems of an application which play an important role in ensuring effective IT observability.
The insights and information collected from different systems help administrators and developers identify threats in real time and at a much early stage.
Further, with this information, developers can optimize code level errors and overall system performance.
Further, it helps keep a quick track of the server performance, network traffic, database issues, and other areas that help ensure the security of IT infrastructure.
Importance of Telemetry in Vulnerability Management
An integrated and comprehensive approach is necessary for vulnerability management as it is a crucial component of business security.
With the use of Telemetry, users can gain critical visibility and information on the security status of different systems. Also, security teams can swiftly detect vulnerabilities as they arise by constantly monitoring and analyzing data from various endpoints, networks, and applications.
With real-time detection, you can reduce possible dangers and the window of opportunity for cybercriminals.
Additionally, organizations can substantially improve vulnerability management efforts by utilizing external telemetry data, which provides information on newly discovered vulnerabilities, exploit strategies, and threat actors.
Telemetry Monitoring Tools
You can find several telemetry monitoring tools online but here are a few things to consider before investing your time and money.
- Make sure its dashboard provides all the insights and system details in real-time.
- It comes with an automation feature that helps find issues and security risks at an initial stage
- Security analytics monitors the patterns, database events, and any suspicious user, and alerts the team
- For informed decision-making, business intelligence provides information regarding security incidents, events and trends
- Log Management utilizes log parsing to translate the log files.
- Supports third-party integrations and historical data analysis
Implementing Telemetry Best Practices
Here are some of the best practices that an organization must follow to maximize the benefits and improve performance.
1. Clear Objectives
Pinpoint all the necessary metrics/KPIs and ensure they align with your set organizational goals and requirements for better productivity and informed decisions.
2. Maintain Data Quality
It is essential to maintain the accuracy and integrity of the collected data and that can be achieved with techniques like data validation.
3. Network Performance Optimization
Another key practice is to ensure that all the data transmission processes take place with minimum latency and network congestion.
4. Maintain Data Security
It is best to invest in tools that come with encryption and authentication mechanisms ensuring no unauthorized users make their way into the system or tamper the crucial files.
5. Regular Maintenance
It is recommended to maintain and test all the telemetry devices for better performance and measurements.
Motadata and Telemetry together can deliver more value
Motadata is one of the trusted IT infrastructure monitoring tools that work well with telemetry data to provide insights into the system performance and application health status.
The robust platform integrates well with practice and ensures better security with optimized IT operations.
By leveraging Motadata’s analytics tools, organizations can unlock great value, address potential performance problems, identify patterns, and monitor user behavior in real time.
Together both telemetry systems and Motadata can make the whole collection, storage, and monitoring process simple and drive more business outcomes.
Telemetry’s contribution to efficiency and sustainability will only grow in importance as technology develops.
At present, many IT administrators and software developers prefer relying on this monitoring practice to gain updates on the performance, health status, and problems of an application.
They use this information to measure the losses, resource consumption, response time, processing time, and the actual status of a system.
FAQs
With the help of this monitoring tool, users can monitor and keep an update on the overall performance of industrial equipment, supply chain logistics, and resource allocation. With all these insights in hand, users can optimize their processes and enhance productivity.
With telemetry, researchers and conservationists can monitor and keep good control over water levels, wind speed, quality of air, and habitat conditions.
The data collected from multiple sources will not only help identify environmental threats at an early stage but also aid in the overall assessment of ecosystem health and taking corrective measures.
Eventually, the minor actions will help reduce ecological risks and preserve biodiversity.