Eliminate Risks With
IT Change Management
Minimize the Risk and Impact of Changes in your IT Infrastructure with our ITIL-aligned Change Management Module that has Dedicated Stages to Bring Control and Increase the Efficiency of Every Rollout.
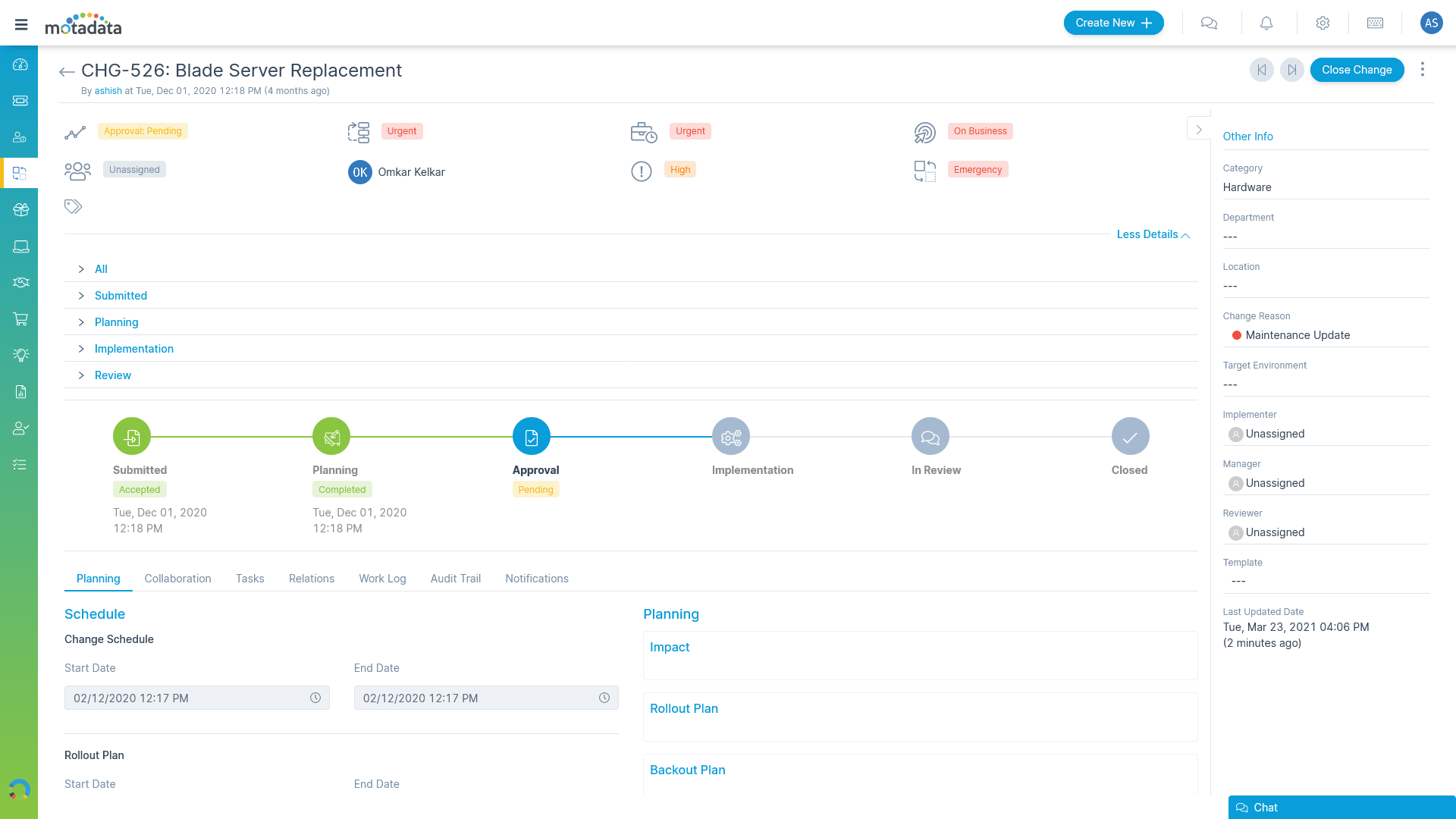
Track Changes through Multiple Stages
Allow your change managers to visually track changes through:
- Highlighted stages
- Stage-wise approvals
- Tracking relationships with other ITIL modules
Key Benefits
- Visibility
- Accountability
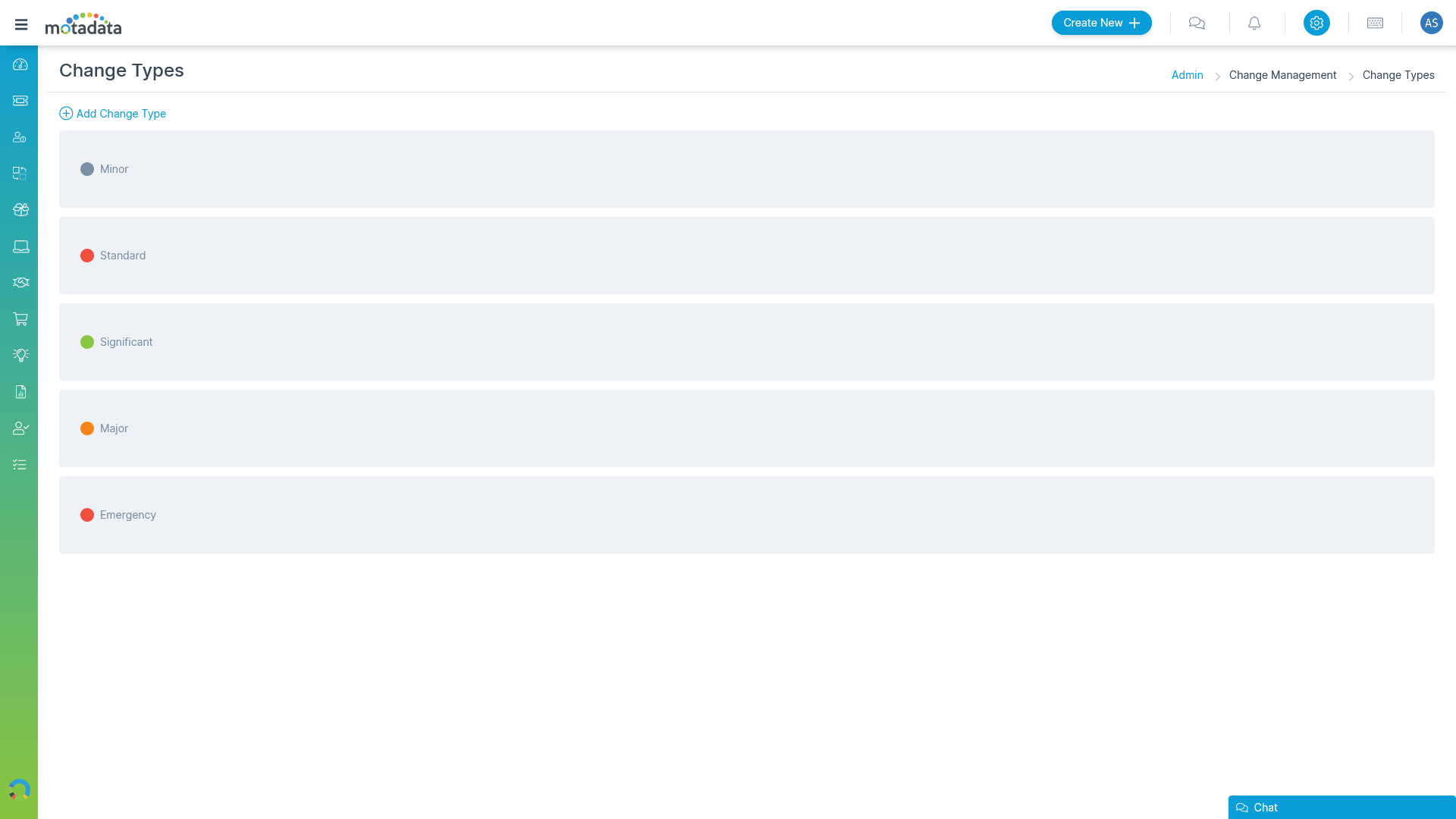
Prioritize Changes based on Change Types
Easily differentiate changes since not all IT changes are the same.
- Create Standard Change
- Create Emergency Change
- Create Significant Change
Key Benefits
- Better Prioritization
- Better Management
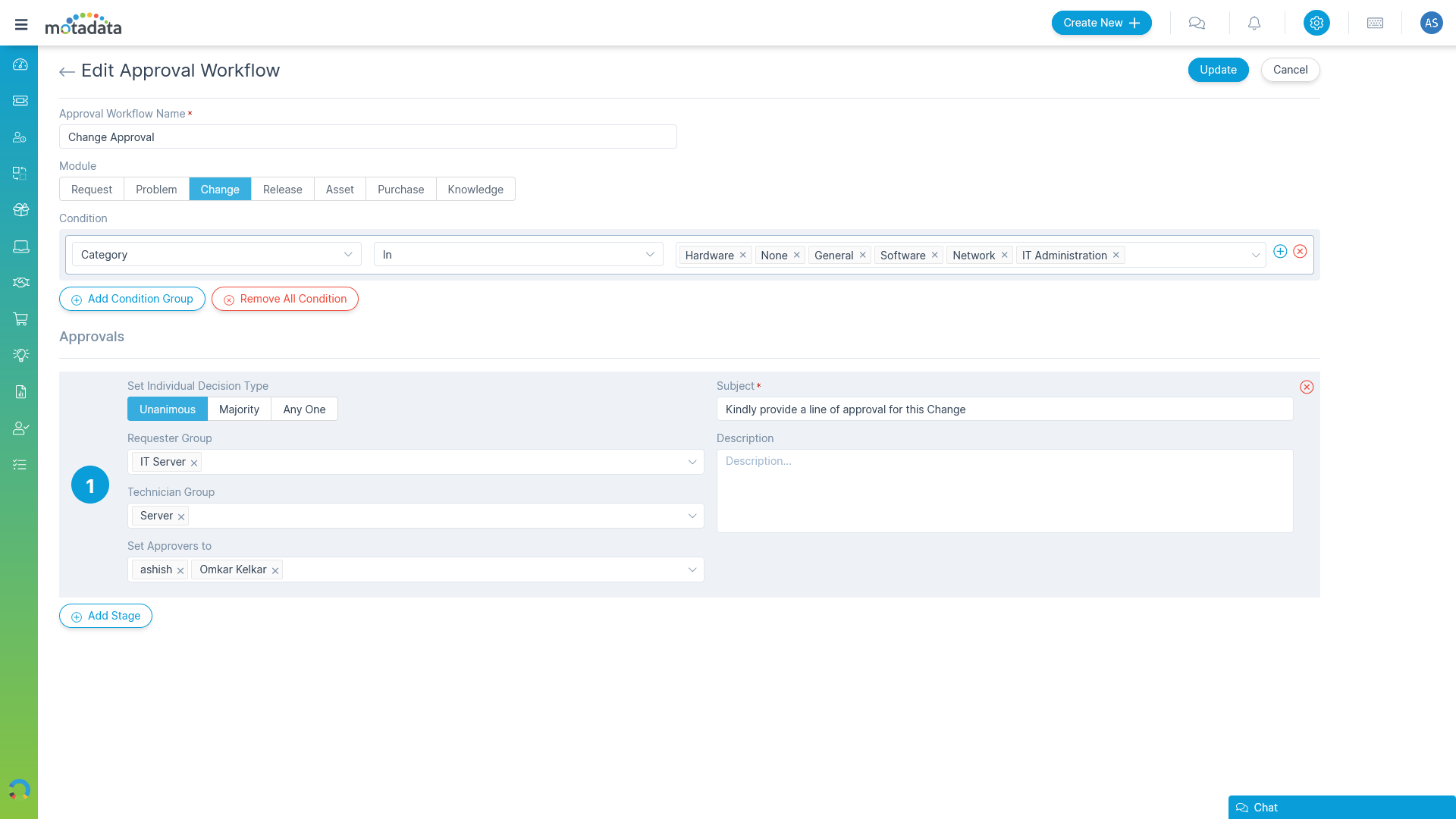
Manage Changes with Advanced Automation
Streamline the life-cycle management of a change using workflows and approvals.
- Auto-change properties based on events
- Dedicated stage for approvals
- Notifications for critical change events
Key Benefits
- Save Time
- Better Control
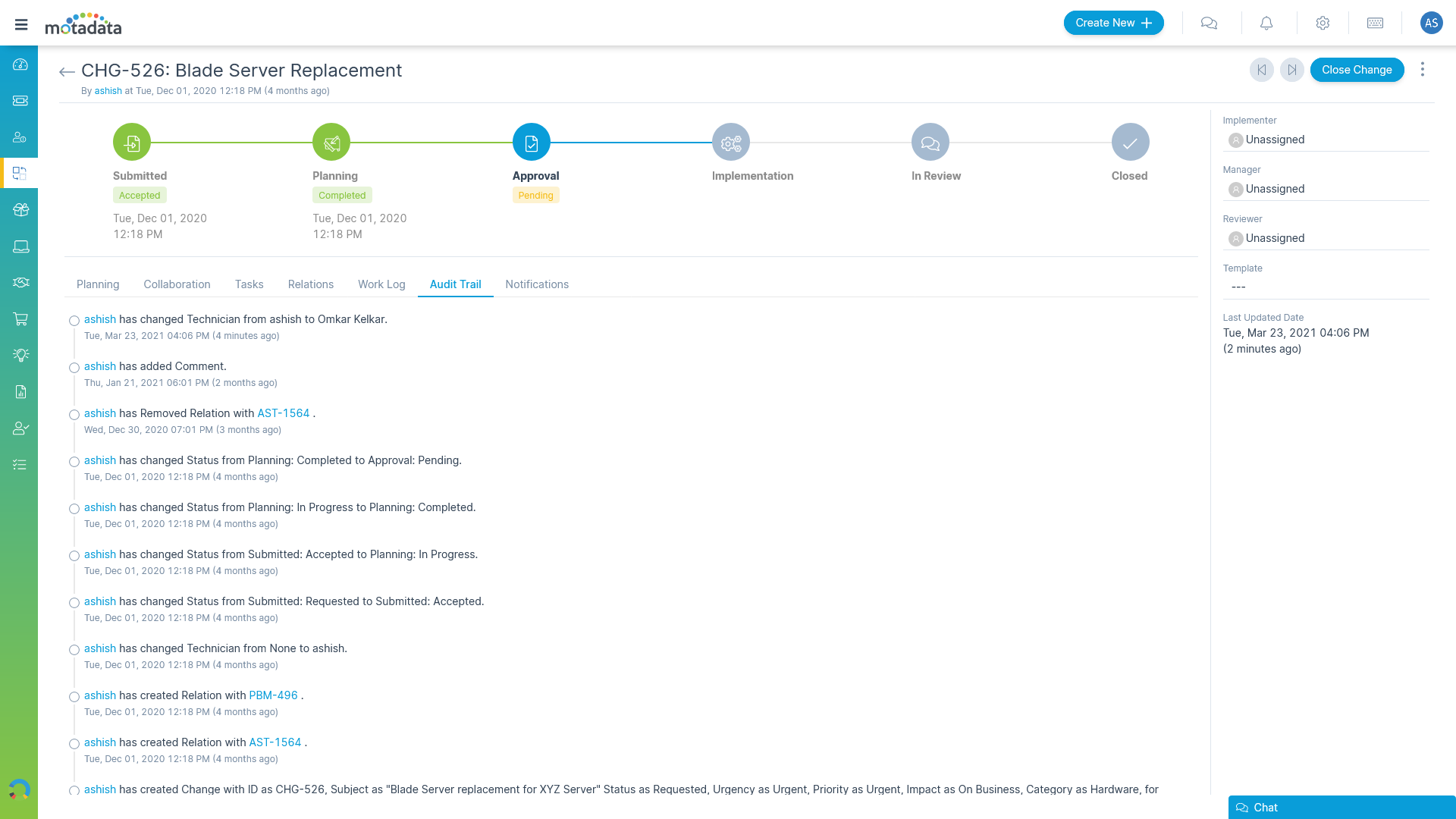
Gain Transparency with Change Information
Acquire relevant information at every step of the change.
- Dedicated stages for schedule and rollout plan
- Audit Trail to track changes
- Assign CAB to a change
Key Benefits
- Transparency
- Easy Access to Information
- Faster Decisions
Improve Your
Service Operation By 30%
Other Features
Bring about a Standard Change Practice in your Organization to Minimize Risk and Maintain Certainty.
Ebook
IT Service Desk, A Complete Guide
A Guide to Supercharge your IT Service Delivery.
Other ServiceOps Modules
Explore ServiceOps
IT service management solution that is easy to use, simple to set up, and has everything you need to provide a seamless IT service delivery experience.
Try ServiceOps for 30 Days
Download our software free of cost for 30 days
Schedule Demo With Our Expert
Book a slot in our calendar and experience ServiceOps live.
Do You Have Any Questions? Please Ask Here We Are Ready to Help You Out
If your question is not listed here, please feel free to reach out.
There are three main types of changes – Standard, Normal, and Emergency Change.
A standard change is a pre-approved, low-risk type of change that adheres to repetitive, documented activities. A normal change, on the other hand, is an intermediary-risk type of change that is not urgent. This change is not pre-approved and requires a thorough review process before approval. The third type of change is the emergency change that is an urgent, high-risk type of change such as security threats.
The Change Manager serves as a facilitator and oversees the whole change management process. His primary responsibilities include authorizing and approving low-risk changes, coordinating and facilitating meetings with the Change Advisory Board (CAB) to address high-risk changes, deciding whether to implement or reject a change, ensuring that all tasks planned to execute the change are following the standards while establishing, recognizing, and evaluating the policies and procedures, preparing a Change Summary Sheet that includes a summary of all RFCs to assist the CAB in comprehending and reviewing the proposed change.
An incident is defined as an unforeseen interruption to a service or decline in the quality of service and a problem is a cause or potential cause of recurring incidents whereas a change is an enhancement, modification, or elimination of anything that can have a direct or indirect impact on ongoing services. Incident management is a reactive process while the problem and change management processes are proactive as well as reactive in nature.
The scope of incident management is to restore normal service operations as soon as possible while the scope of problem management is to identify the root cause of service disruptions. The scope of change management, on the other hand, is implementing a change to address the root cause to avoid further interruptions to normal service operations.
ITIL change management best practices include understanding why the change is being recommended. Every change request should be evaluated in terms of what value it offers and what kind of risks it presents. After understanding the purpose of the change, organizations can quantify changes using appropriate KPIs and metrics. Change metrics can help in tracking ongoing trends, providing information about resource allocation, and measuring the change performance.
Predictive IT analytics can enable organizations to quantify change risks and understand their impact on normal service operations. This helps the organization in identifying the appropriate response like accepting the change risk, decreasing the risk by modifying the change or preventing the risk by stopping the change altogether until it presents less risk. Finally, each change needs to have a closure process whether it is successful or not.
