Overview
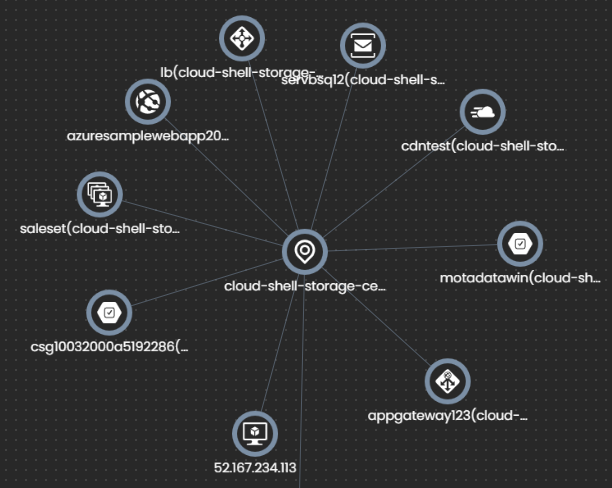
A visual representation of the network infrastructure helps you find the relationship between different elements of your network which in turn helps you to gain a better understanding of the same. This customizable visual representation of your architecture is achieved in Motadata through a Topology map.
Current networks are large, dynamic, and complex with ever-changing components. Under these circumstances, it becomes difficult to achieve optimum performance and network health to ensure business continuity. A comprehensive view of the network then becomes essential and a network topology map can provide this.
Topology maps are dynamic in nature to reflect the current state of your system without having to make manual changes in the network topology when the components of your infrastructure change. The topology reflects the latest links and device status subject to the timely run of the topology scanner.
These maps depict the relationship between the various infrastructure components including switches, routers, firewalls, virtual devices, and cloud services.
These real-time topology maps can be used to visualize complete IT infrastructure, locate the root cause of the issue quickly and efficiently and help you decide on a fix for the same.
The protocols supported for creating a topology map of a network device in Motadata are:
- Layer 2 protocols
- Cisco Discovery protocol
- Link Layer Discovery protocol
- Switch Port Mapping protocol
- Layer 3 protocols
- Open Shortest Path First protocol
- Border Gateway protocol
- Intermediate System to Intermediate System protocol
The protocols supported for creating a topology map of a virtual device in Motadata are:
- Hyper-V
- VMware
- Citrix Xen
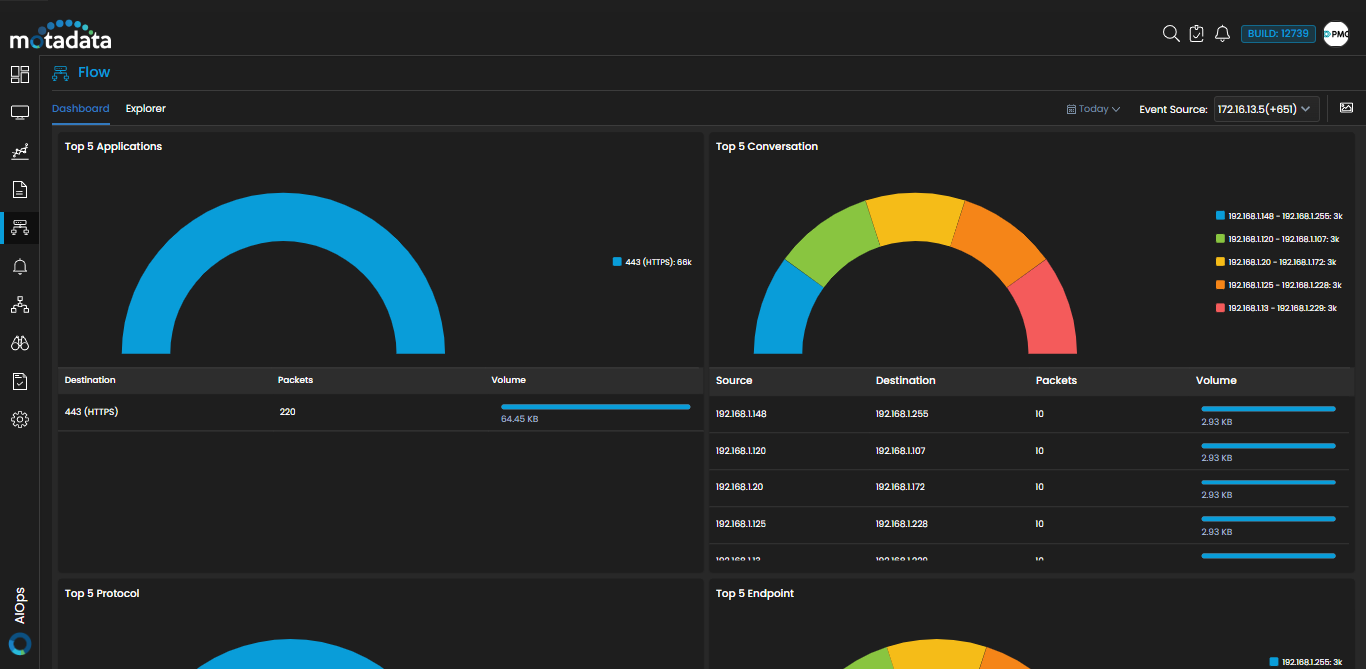
![]() . The Flow Dashboard screen is now displayed.
. The Flow Dashboard screen is now displayed.