IT asset management is an essential component to consider in every organization, regardless of the size and type of its business.
Managing IT assets is critical in today’s technology-dependent business environment, as these assets underpin business advancement and efficiency.
Starting with hardware systems such as servers and laptops and ending with software programs, applications, and cloud resources, these assets’ management is critical to maximizing relevant value while keeping expenses at a bare minimum.
ITAM identifies, manages, and disposes of IT assets throughout their life cycle. It involves identifying the assets, monitoring and managing them, and finally disposing them.
By utilizing ITAM, an organization can adequately use IT resources, properly utilize the data centers, and make decisions regarding future asset purchases.
In the following blog, we will look at ITAM definitions, various categories of IT asset data, the components of ITAM, and the advantages of effective asset management processes will also be described.
For Information Technology (IT) professionals and managers aiming at improving the ability of their organizations to manage firm’s IT properties or the business executives aspiring to make improvements in the management of IT assets, this guide is designed to arm you with all the information and knowledge you require in the field of ITAM.
What is IT Asset Management (ITAM)?
IT Asset Management (ITAM) can be described as a governance process for managing IT-related assets within an organization.
It entails identifying IT assets and monitoring them from their acquisition until they are disposed of.
ITAM’s objective is to help organizations maintain a record of all their IT assets to assist them in outputting the best results concerning the investments made in the IT sector.
ITAM involves many activities, such as identifying, tracking, and maintaining assets and retiring assets.
Having an ITAM practice, which in other words means an organization can track, document, analyze, and store information about its IT assets, will help it make concrete decisions on how to manage IT assets, how to use them, and whether to buy them, maintain them, or throw them away.
ITAM has strong links with IT service management (ITSM) since both fields are centered on IT asset management. Both aim to provide effective services required to support an organization.
While ITSM is all about providing and supporting IT services, ITAM is specific to the management and governance of IT assets.
The IT Asset Management Process
The IT Asset Management (ITAM) process is a structured set of activities that enables organizations to track, manage, and optimize IT assets throughout their lifecycle. By standardizing this process, businesses can improve asset visibility, control costs, enhance compliance, and ensure IT resources support both operational and strategic objectives. The ITAM process also serves as the execution layer of the IT Asset Management framework, translating governance and policy into actionable steps.
Inventory Assets
Inventorying assets is the first and most critical step in the IT asset management process. It involves identifying, recording, and maintaining a centralized inventory of all IT assets, including hardware, software, and cloud-based resources. A comprehensive asset inventory provides accurate information about asset location, ownership, configuration, and usage, forming the foundation for effective tracking, compliance, and lifecycle management.
Calculate Lifecycle Costs
Calculating lifecycle costs helps organizations understand the total cost of ownership (TCO) of IT assets. This includes procurement, deployment, licensing, maintenance, upgrades, support, and disposal costs. Lifecycle cost analysis enables better budgeting, cost optimization, and data-driven decisions when purchasing, renewing, or retiring assets.
Track Assets
Asset tracking ensures continuous visibility into asset movement, usage, and status throughout their lifecycle. Real-time tracking helps organizations identify underutilized assets, prevent loss or misuse, improve security, and support audit readiness. Effective tracking also strengthens compliance and risk management practices.
Maintenance
Maintenance focuses on sustaining IT assets at optimal performance levels. This includes routine updates, patching, repairs, and performance monitoring. Proactive maintenance reduces downtime, extends asset lifespan, and minimizes operational disruptions while supporting security and reliability.
Financial Planning
Financial planning aligns IT asset investments with business goals and budgets. It includes forecasting asset requirements, managing depreciation, planning renewals, and optimizing IT spend. Strong financial planning ensures IT assets deliver maximum value while controlling costs and supporting long-term growth.
What are the categories of IT Asset Management?
The IT Asset Management system’s transactions can be categorized into different types depending on the nature of the assets. The main types of ITAM include: The main types of ITAM include:
Software
Though ITAM is a comprehensive practice, Software Asset Management (SAM), a part of ITAM, is mainly concerned with managing software assets in an organization.
This includes their usage in other applications, licensing, and compliance with software usage agreements.
SAM entails the identification and control of software assets from their acquisition to their withdrawal. Software asset management, license management, usage/ reporting, and contract management are some elements.
Hardware
Hardware Asset Management is the process of overseeing tangible IT commodities in an organization. These include servers, PCs, laptops, mobile communication devices, and networking hardware.
Organizations must have a clear picture of each piece of their hardware assets, including where it is, how often it is used, the composition of its maintenance history, and at what stage of its life cycle.
Having the correct information about an organization’s H/W can help the organization make the right decisions about the H/W assets in its possession in terms of acquisition, maintenance, and disposal.
Digital Assets
Digital Asset Management targets managing digital assets within an organization. It champions data, information technology systems, databases, and other technological assets.
Digital assets are part of the current organizational reality, and it remains crucial for modern companies to manage them properly to guarantee high data quality, nonlegal compliance, and smooth business processes.
It includes data inventory control, governance, security, and metadata control.
IT Asset Management Framework
An IT Asset Management (ITAM) Framework provides a structured and standardized approach to managing IT assets throughout their entire lifecycle. It acts as a blueprint that aligns people, processes, technology, and governance to ensure IT assets deliver maximum value while minimizing cost, risk, and compliance issues.
A well-defined ITAM framework helps organizations move from reactive asset tracking to proactive, data-driven asset governance.
Core Pillars of an IT Asset Management Framework
An effective ITAM framework is built on the following foundational pillars:
1. Governance and Policy Management
Governance defines who owns the assets, how they are managed, and which rules apply.
Key elements include:
- Asset ownership and accountability
- IT asset policies and standards
- Compliance with regulatory and licensing requirements
- Defined roles and responsibilities across IT, finance, and procurement teams
Strong governance ensures consistent asset handling and reduces legal, financial, and operational risks.
2. Asset Discovery and Inventory Control
Asset discovery is the foundation of the ITAM framework. It ensures complete visibility into all IT assets across the organization.
This includes:
- Automated discovery of hardware, software, and cloud assets
- Centralized and continuously updated asset inventory
- Tracking asset location, status, configuration, and usage
- Identifying unauthorized or shadow IT assets
Accurate inventory data enables informed decision-making and prevents asset sprawl.
3. Lifecycle Management
Lifecycle management ensures IT assets are managed efficiently from planning to retirement.
This covers:
- Planning and demand forecasting
- Procurement and deployment
- Operational usage and maintenance
- Renewal, replacement, or retirement
A structured lifecycle approach helps organizations extend asset life, reduce downtime, and avoid unnecessary purchases.
4. Financial Management and Cost Optimization
Financial visibility is a critical component of the ITAM framework.
Key aspects include:
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) analysis
- Budgeting and forecasting
- Depreciation tracking
- Chargeback or showback models
By aligning financial data with asset usage, organizations can optimize spending and improve ROI on IT investments.
5. Software Asset and License Management
Software assets represent a significant cost and compliance risk.
This pillar focuses on:
- License entitlement and usage tracking
- Preventing over-licensing and under-licensing
- Audit readiness and compliance management
- Managing SaaS subscriptions and renewals
Effective license management reduces audit exposure and eliminates wasted software spend.
6. Risk, Security, and Compliance Management
ITAM plays a critical role in strengthening an organization’s security posture.
This includes:
- Identifying end-of-life and unsupported assets
- Supporting vulnerability and patch management
- Ensuring secure asset disposal and data sanitization
- Maintaining audit trails and compliance documentation
Asset visibility is the foundation of effective risk and security management.
7. Automation and Integration
Modern ITAM frameworks rely heavily on automation and system integration.
This involves:
- Automated asset discovery and updates
- Integration with ITSM, CMDB, procurement, and finance systems
- Automated reporting, alerts, and compliance checks
Automation reduces manual effort, improves data accuracy, and accelerates decision-making.
8. Performance Measurement and Continuous Improvement
An ITAM framework must evolve with the organization.
This pillar focuses on:
- Defining ITAM KPIs and success metrics
- Regular audits and performance reviews
- Stakeholder feedback loops
- Continuous process optimization
Measuring performance ensures the ITAM program delivers ongoing value and supports business growth.
Aligning IT Asset Management Framework with Business Objectives
A mature ITAM framework aligns IT asset strategies with broader business goals such as:
- Cost optimization
- Operational efficiency
- Regulatory compliance
- Scalability and digital transformation
When implemented effectively, the ITAM framework becomes a strategic enabler, not just an operational function.
Why an IT Asset Management Framework Is Essential
Without a structured framework, organizations risk:
- Poor asset visibility
- Compliance violations
- Uncontrolled IT spending
- Increased security vulnerabilities
An IT Asset Management Framework ensures control, transparency, and accountability, empowering organizations to manage IT assets proactively and strategically.
Important Components of IT Asset Management
IT Asset Management consists of multiple critical components for proper functioning and business organization. These components include:
Asset Discovery
ITAM is comprised of several processes, one of which is Asset Discovery. It can be defined as mapping and documenting all IT resources in organizations, from hardware to software and even cloud.
When all assets are located and documented systematically, organizations can learn about their IT assets’ condition and improve their distribution, making the right decisions about asset purchase and disposal.
Asset Inventory
Asset Inventory can be defined as the process of developing and updating the inventory of an enterprise’s IT assets.
These include server hardware, client hardware, PCs, laptops, and any other handheld devices used in performing business functions.
Ideal asset inventory management will provide an organization with honest and timely details about the location, attributes, usage, and maintenance records of its IT assets.
Asset Lifecycle Management
Asset Lifecycle Management is a subprocess of IT Asset Management that deals with an organization’s lifecycle of assets.
It entails acquiring technologies, implementing them within the organization, supporting, sustaining, and phasing them out.
This is important for hardware assets since they are high-value and fragile and mainly get used over time in an organization. For this reason, they need to be adequately managed.
License Management
License Management is a sub-discipline of IT Asset Management used to manage an organization’s software licenses.
Good and proper License Management guarantees the installation of as many permits as possible per the agreements and ensures that as many licenses as possible are used optimally.
Effective License Management practice means non-interference with the organization’s compliance, eradicating the risk of fines or penalties, and efficiently utilizing the available licenses to achieve maximum ROI.
Compliance and Audit Management
Compliance and Audit Management is one of the modules of IT Asset Management that deals with managing regulatory provisions, compliance with governance rules and frameworks, and preparation for software audits.
Practical Compliance and Audit Management is crucial for managing and addressing legal and regulatory requirements, avoiding penalties for non-compliance, and achieving sound corporate governance.
What is an ITAM Database or SAM Database?
An ITAM Database is, therefore, the management and central data source or records of IT assets in an organization.
This entails physical, financial, and contractual details of IT assets within an organization’s asset register, thus providing a complete profile of the organization’s IT assets.
The spacious part of an ITAM Database encompasses all the details surrounding the tangible assets within a company, which include the details of the hardware and the software implemented in the organization, including product details, physical location, and usage.
The last component is the financial component, which concerns the monetary aspects of IT assets; these include the costs of acquiring the assets, the depreciation, and the charging of fees.
Physical
Tangible resources are a key aspect of the IT asset management framework. They are crucial for protecting data, maximizing business efficiency, and reducing costs.
Hardware resources include all physical computer and data processing and related equipment, such as servers, PCs, laptops, PDAs, printers, scanners, and keyboards.
Such assets are helpful for an organization’s business processing and information technology activities.
Nonetheless, when people poorly manage such physicals, they can depreciate, become underutilized, or even pose a security threat.
Financial
Budgeting is an imperative issue in managing IT assets. It covers managing and consolidating information technological assets’ financial performance, aiming at cost reduction and increased value addition to organizational performance.
Thus, total cost of ownership (TCO) is one of the parameters considered in the IT asset management process. It relates to all costs incurred in procuring and implementing IT resources, supporting them, and disposing of them.
Analyzing the TCO of IT assets provides the necessary information to improve asset management in an organization, for example, through money-saving activities, rational use of IT assets, and avoidance of unnecessary costs.
Contractual
One component of ITAM coverage is contractual management. It concerns monitoring and administrating multiple contracts and relations in a structure connected with IT assets, including licenses, SLAs, and vendors’ contracts.
In ASNs, contract management is a critical element that helps to enforce compliance and adequately use the IT assets.
This formal legal document specifies the different rules and parameters of software application use, including the number of licenses to be availed, the installation allowed, and other limitations.
Therefore, handling license agreements well helps organizations to be legal to avoid being penalized for infringement on licenses and helps in the correct use of licenses on software.
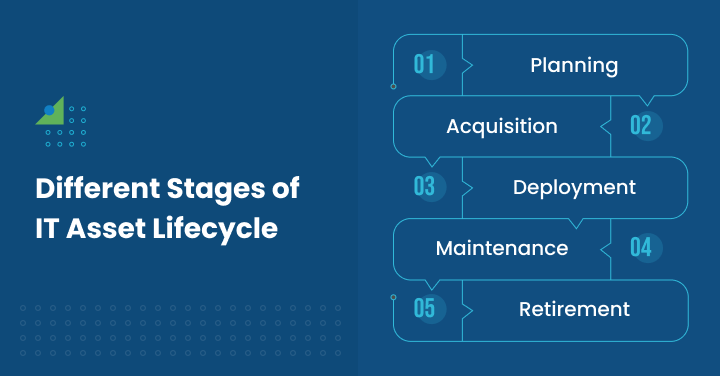
Different Stages of IT Asset Lifecycle
The life cycle of an IT asset covers several stages: acquisition, implementation, utilization, maintenance, obsolescence, and disposal. All stages are essential in improving IT assets’ management and usage efficiency.
The I&T asset may be in the planning or acquisition phases, already deployed, used, and maintained, or it has reached its useful life and is ready to be retired.
Planning
Planning is one of the most essential phases of the life cycle of existing IT assets.
The organization’s requirements, how these resources will be employed, and how they will be obtained are all determined by managerial decisions.
Planning also encompasses competitive options assessment, cost/benefit and TCO analysis, and proper scheduling by the company’s targets and processes for acquiring the assets.
Acquisition
This is a critical stage of the IT asset life cycle, as owning assets is as significant as getting them. It includes the purchasing process of getting the IT facilities and equipment, whether computer hardware or software, required in an organization.
Strategic acquisition involves efficient procurement methods, the management of supplies, and the costs involved.
Deployment
The final process of the IT asset life cycle is deployment. It relates to incorporating information technology resources and components like applications and equipment into an organization’s structures.
The IT department efficiently runs when proper utilization optimally uses the implemented resources.
Maintenance
The maintenance stage of IT assets’ lifecycle is critical. It covers a process of renewing, refurbishing, and constantly preserving IT properties for the specified optimum level of practical use and durability. Practical maintenance mainly consists of technical help, new program installation, and checkups.
Retirement
The final phase of the IT asset is retirement. It refers to an organization’s process and exercise of getting rid of IT assets that are either obsolete or otherwise redundant or superfluous.
Good retirement also confirms information safety, adherence to the set law, and proper disposal of assets.
What are the Benefits of IT Asset Management?
IT assets quietly grow in the background—new laptops are issued, software subscriptions renew automatically, and cloud resources expand as teams scale. Over time, what once felt manageable becomes difficult to control. This is where IT Asset Management (ITAM) begins to show its real value, not as a technical process, but as a practical way to bring order, clarity, and confidence back into IT operations.
1. Improves Utilization and Cuts Risks
IT teams often discover that a significant portion of their assets are underused or forgotten altogether. IT asset management changes that by making every asset visible. When teams know what they own and how it’s being used, they can reuse existing resources instead of buying more. At the same time, outdated systems, expired licenses, and unsupported devices are easier to spot and fix before they turn into security incidents or audit issues.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
As businesses grow, IT needs rarely stay the same. New employees join, projects expand, and infrastructure demands increase. With ITAM in place, scaling becomes far less chaotic. Teams can plan ahead, understand capacity limits, and add new assets without losing control. The result is an IT environment that can grow and adapt without constant firefighting.
3. Supports IT and Business Practices and Enables Teams
When IT asset information is scattered, teams waste time searching for answers. ITAM brings everyone onto the same page. IT, finance, procurement, and compliance teams can rely on a single source of truth. This shared visibility helps employees get the tools they need faster and allows teams to work together more effectively.
4. Better Vendor Management
Vendor relationships improve when asset data is clear. With accurate records of licenses, contracts, and renewals, organizations avoid surprise costs and last-minute negotiations. This visibility makes it easier to hold vendors accountable and secure better terms over time.
5. Strategic Planning and Alignment
Over time, ITAM shifts from solving daily problems to supporting bigger decisions. Leaders can see trends, understand costs, and plan investments with confidence. IT assets stop being an expense to manage and become resources that actively support business goals.
What are The IT Asset Management Best Practices?
Adopting IT Asset Management (ITAM) best practices enables organizations to gain better visibility, control costs, reduce risks, and ensure compliance across the entire asset lifecycle. By standardizing processes and aligning teams, organizations can transform ITAM from a reactive activity into a strategic capability. Below are the essential best practices for building an effective IT asset management program.
1. Constitute the Pilot Project Team
Start with a pilot project team to validate ITAM processes before full-scale implementation. This cross-functional team should include members from IT, finance, procurement, and compliance. A pilot helps identify gaps, test workflows, and refine processes in a controlled environment, reducing risk during enterprise-wide rollout.
2. Identify Key Assets
Not all assets carry the same level of importance. Organizations should identify and prioritize critical assets that directly support business operations or pose higher compliance and security risks. Maintaining detailed records of these assets ensures focused monitoring, better protection, and informed decision-making.
3. Select Discovery and Integration Techniques
Automated discovery tools are essential for accurately identifying hardware, software, and cloud assets. Equally important is integrating ITAM with ITSM, CMDB, procurement, and finance systems. Strong integration ensures consistent data flow, reduces duplication, and improves operational efficiency.
4. Maintain Continuous Asset Tracking
Continuous tracking provides real-time visibility into asset location, usage, and status. This practice helps identify underutilized or unauthorized assets, supports audits, improves security, and enables proactive asset optimization throughout the lifecycle.
5. Establish Clear Policies and Procedures
Clear ITAM policies define how assets are acquired, used, maintained, and retired. Well-documented procedures ensure consistency, accountability, and compliance across departments while reducing dependency on individual knowledge.
6. Maximize Automation
Automation reduces manual effort and improves accuracy across asset discovery, inventory updates, license tracking, reporting, and alerts. By automating routine tasks, IT teams can focus on strategic initiatives rather than administrative work.
7. Collect Feedback for Improvement
Continuous improvement depends on feedback from IT teams, end users, and stakeholders. Regular reviews, surveys, and performance assessments help identify gaps and refine ITAM processes to better support business needs.
Factors to Consider While Selecting the Right IT Asset Management Solution Provider
Selecting the right IT asset management solution provider is crucial for organizations looking to implement an effective ITAM strategy. Here are some key factors to consider:
Functionality: Evaluate the features and capabilities of the ITAM software the solution provider offers. Ensure that it meets your organization’s specific requirements and can handle the complexity of your IT environment.
Scalability: Consider the scalability of the solution provider’s software. Will it accommodate your organization’s growing IT asset inventory and changing needs over time?
Integration: Check if the ITAM software can integrate with your existing IT systems, such as help desk software, procurement systems, and configuration management databases. Integration capabilities can streamline processes and enable better data synchronization.
Customization: Determine if the solution provider offers customization options to tailor the ITAM software to your organization’s unique needs. Customization can enhance the software’s usability and efficiency.
Reporting and Analytics: Assess the IT asset management software’s reporting and analytics capabilities. It should provide comprehensive insights into asset utilization, compliance, and financial performance, enabling data-driven decision-making.
Customer Support: Consider the level of technical support and customer service the solution provider provides. Timely assistance and reliable support are essential for smooth implementation and ongoing software maintenance.
The Impact of AI on IT Asset Management
IT asset management has long relied on manual effort, periodic audits, and static reports. As IT environments grow more dynamic, with cloud platforms, remote workforces, and subscription-based software, these traditional approaches struggle to keep pace. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is changing this reality by making IT asset management smarter, faster, and more proactive.
Smarter Asset Discovery and Visibility
AI enhances asset discovery by continuously scanning IT environments to identify hardware, software, and cloud assets in real time. Unlike manual or rule-based methods, AI adapts to changes automatically, ensuring asset inventories remain accurate and complete. This improved visibility helps organizations eliminate blind spots, detect shadow IT, and maintain control over rapidly changing IT ecosystems.
Predictive Maintenance and Cost Optimization
By analyzing historical data and usage patterns, AI enables predictive maintenance and smarter cost management. It can forecast hardware failures, identify assets nearing end-of-life, and highlight underutilized resources. These insights allow IT teams to act before issues arise, reduce downtime, avoid unnecessary purchases, and extend asset lifecycles, resulting in significant cost savings.
Intelligent Compliance and Decision-Making
AI strengthens compliance and governance by monitoring license usage, identifying anomalies, and flagging potential risks early. In addition, AI-driven insights transform raw asset data into clear recommendations, helping IT leaders make informed decisions quickly. Rather than reacting to problems, organizations can plan strategically and align IT asset management more closely with business objectives.
How can Motadata help you make IT Asset Management Simple for you?
IT Asset Management often starts with good intentions but quickly turns into a challenge. Spreadsheets grow outdated, assets go missing, licenses become difficult to track, and audits arrive with little warning. This is the situation many organizations face as their IT environments expand. Motadata steps in to simplify this complexity by turning IT asset management into a clear, structured, and manageable process.
From Scattered Assets to Complete Visibility
Imagine an IT team struggling to keep track of laptops, servers, applications, and licenses spread across departments and locations. With Motadata, that confusion disappears. The platform automatically discovers hardware and software assets and brings them together into a single, centralized view. IT teams no longer need to rely on manual updates or guesswork—they can instantly see what assets exist, where they are, and how they are being used, restoring control and confidence.
Managing the Entire Asset Lifecycle with Ease
As assets move through procurement, deployment, usage, and retirement, Motadata quietly keeps everything on track. Warranties nearing expiration, licenses approaching renewal, or assets reaching end-of-life are no longer surprises. Automated lifecycle and license management ensure compliance, reduce unnecessary spending, and help organizations get the most value from every IT investment—without adding extra operational burden.
Turning Data into Decisions
Instead of reacting to problems, organizations using Motadata start planning ahead. Clear dashboards and reports reveal underutilized assets, compliance gaps, and cost-saving opportunities. The intuitive interface makes adoption easy, even for non-technical users, while reliable support ensures help is always available. With Motadata, IT asset management shifts from a daily struggle to a strategic advantage—simple, predictable, and efficient.
FAQs
By maximizing asset use, preventing pointless acquisitions or upgrades, and prolonging the life of IT assets, ITAM can assist in lowering organizational expenses. As a result, there are financial savings as well as operational and return on investment gains. By comprehending the total cost of ownership and making wise asset management decisions, organizations can cut costs significantly.
Correct asset inventory, efficient asset lifecycle management, thorough compliance management, and accurate inventory are essential elements of a successful ITAM program. These elements guarantee that businesses have total visibility and control over their IT resources, which promotes program success and efficient asset management.
ITAM allows companies to comply with regulations by tracking usage, keeping correct records of their IT assets, and ensuring that the law is followed. By offering thorough information and assisting with audit readiness, ITAM assists firms in meeting regulatory compliance criteria and avoiding penalties or fines.
Process optimization, less errors, automated asset tracking, and enhanced process efficiency are just a few advantages of automating IT asset management procedures. Automation improves accuracy, expedites asset management processes, and helps businesses run their IT asset management procedures more productively and efficiently.