In today’s digital world, applications play a vital role in business operations. Whether it’s an internal tool used by employees or a customer-facing application, the performance of these applications directly impacts user experience, business outcomes, and overall productivity.
Application Performance Monitoring (APM) is a critical practice that ensures applications meet the performance, reliability, and user experience standards required by employees, partners, and customers.
APM involves the collection of tools and processes designed to monitor and manage the performance of enterprise applications. It allows IT professionals to track various metrics, identify performance issues, and quickly resolve them to optimize application performance.
By monitoring key performance indicators such as response time, CPU usage, and error rates, APM tools provide valuable insights into application health and help organizations proactively address any performance issues.
With the increasing complexity of modern applications, APM has become essential for maintaining a seamless user experience.
In this blog, we will explore the definition of APM, its importance, how it works, its benefits and challenges, and the different types of APM tools available in the market.
Definition: What is Application Performance Monitoring
Application Performance Monitoring (APM) is the practice of monitoring and managing the performance and availability of software applications.
It involves the use of specialized tools and techniques to track key performance indicators, identify performance bottlenecks, and resolve issues that may impact user experience and business outcomes.
APM focuses on monitoring various aspects of application performance, including response time, CPU usage, memory utilization, error rates, and network latency.
It provides real-time visibility into the performance of individual components, as well as the overall application architecture.
By collecting and analyzing performance data, APM tools help IT teams understand how applications are performing, identify areas for improvement, and take proactive measures to enhance performance and user experience.
Application performance monitoring is crucial for ensuring that applications meet the performance requirements set by stakeholders, such as end users, business partners, and customers.
It allows organizations to maintain high standards of availability, responsiveness, and reliability, thereby maximizing user satisfaction and minimizing the negative impact of performance issues on business operations.
Overall, APM plays a vital role in optimizing application performance, enhancing user experience, and enabling organizations to deliver high-quality software applications that meet the expectations of their users.
Why Application Performance Monitoring is important?
Application Performance Monitoring (APM) is important for several reasons. First and foremost, it ensures a positive user experience by monitoring and optimizing application performance.
In today’s digital landscape, users have high expectations when it comes to the performance of applications.
They expect applications to be fast, responsive, and reliable. If an application is slow or experiences frequent performance issues, users may become frustrated, leading to dissatisfaction and potentially impacting business outcomes.
APM is also important for business outcomes. Poor application performance can directly impact revenue, customer satisfaction, and brand reputation.
When applications are slow or inaccessible, users may abandon transactions, leading to lost sales and revenue. Additionally, negative user experiences can damage a company’s reputation and lead to decreased customer loyalty.
By monitoring and optimizing application performance, organizations can ensure that their applications meet the performance standards necessary for achieving business success.
How does APM work?
Application Performance Monitoring (APM) works by continuously monitoring and analyzing the performance of software applications.
It involves the collection of performance data from various sources, such as servers, databases, and network devices, and the analysis of this data to identify performance bottlenecks and potential issues.
APM tools collect performance data from different components of an application, including server metrics, database queries, network latency, and user interactions.
This data is then aggregated, analyzed, and visualized to provide insights into the overall performance of the application.
By monitoring key performance indicators, such as response time, error rates, and CPU utilization, APM tools enable IT teams to identify performance issues and take appropriate actions to resolve them.
Effective APM involves a combination of automated monitoring, real-time alerting, and proactive performance optimization.
APM tools continuously monitor performance metrics and generate alerts when performance thresholds are exceeded or anomalies are detected.
These alerts help IT teams quickly identify and respond to performance issues, minimizing the impact on end users.
To ensure effective APM, organizations need to define relevant performance metrics, set performance thresholds, and establish performance baselines.
By monitoring these metrics and comparing them against the predefined thresholds and baselines, organizations can proactively identify potential performance issues and take preventive actions.
Overall, APM works by monitoring and analyzing performance data to identify performance bottlenecks, optimize application performance, and ensure a smooth user experience.
By implementing effective APM practices, organizations can deliver high-quality applications that meet user expectations and support their business goals.
What does APM do?
System administrators and developers can diagnose, monitor, and optimize the overall performance of their applications using this robust APM tool.
It uses machine learning and artificial intelligence techniques to monitor and analyze how users interact with applications as well as discover bugs and other problems that may impact user-end experience.
It further provides actionable insights into the application health, component status, response time, resource usage, error rate, and other aspects that play a key role in application performance.
With this useful solution, developers can even keep a real-time watch over the frontend as well as backend components of applications.
Here are a few more key features of Application Performance Monitoring tools:
- Visualize application topology – The tool provides a 360-degree view of the application and its architecture that helps in better understanding of the workflow anomalies and external dependencies.
- AI-powered Troubleshooting – It helps quickly identify unusual user behavior with AI techniques and machine learning, enabling developers to take corrective measures before they affect end-user experience. It even helps keep track of user interactions with the application and meets the unique needs for better business outcomes.
- Distributed Tracing – With this powerful solution, developers can even keep a good track of all transactions that take place across both microservices and distributed architecture.
Five Elements of APM:
1. End-user experience monitoring: As per a Gartner survey, end-user experience monitoring is the most critical element of the APM. It collects information on how end-users interact with the application, identifying any problems.
2. Runtime Application Architecture Discovery: This element of APM understands the application’s architecture and how different components interact during the runtime. With this, it becomes easy to identify dependencies and possible performance bottlenecks.
3. User-Defined Transaction Profiling: User-defined transactions traverse the architecture, which is why they are more important than we think. Transaction profiling refers to tracking individual user transactions or requests to understand when and where the events occur.
4. Component Deep-Dive Monitoring: This element involves monitoring and analysing specific application components, such as databases, servers, or third-party integrations. It offers insights into the performance of each segment, allowing for targeted optimizations.
5. Analytics: Simply having information is not enough; you need to make sense out of it – this is when analytics plays a role. It collects and analyses performance data, providing valuable trends, patterns, and correlations that aid in making informed decisions for application optimization.
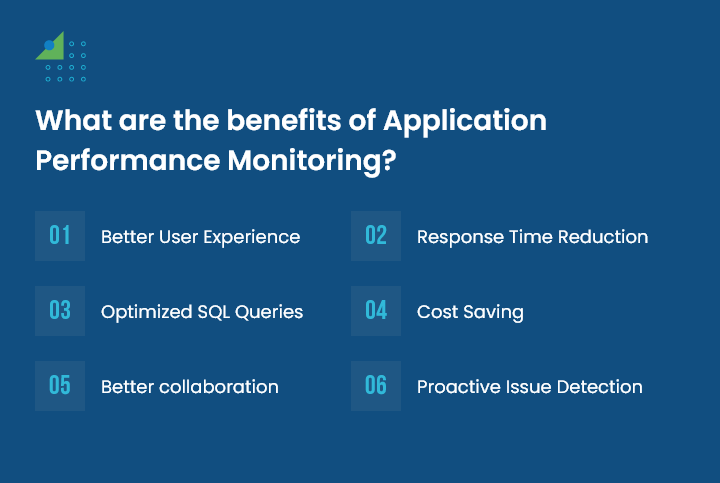
What are the benefits of APM?
APM offers several benefits to organizations in terms of performance management, business outcomes, and user experience.
1. Better User Experience
By monitoring each and every application and its components, developers can track the faults and fix the errors in real-time ensuring a smooth and seamless user experience.
Further, they could track the response time, latency, and other potential performance problems that might impact user satisfaction.
2. Response Time Reduction
These tools are capable of monitoring several endpoints and business transactions on a constant basis, resulting in faster detection of bottlenecks and code level errors.
These faults in the application often contribute to high response time. However, with APM’s real-time alert options, team members can address the performance problems in real time and reduce the response time.
3. Optimized SQL Queries
The tool provides in-depth visibility into the performance of SQL queries and identifies the potential problems in real time.
Most of these tools also offer query profiling and tracing capabilities that make it easy for organizations to trace the path and resolve complex queries.
SQL query optimization reduces the load time of the database and enhances the application responsiveness which results in quick performance of an application.
4. Cost Saving
With clear insights on resource usage, computing power, infrastructure, and other aspects essential for the smooth running of applications, businesses can save on operating costs and reduce them to a minimum.
Further, any expense associated with the downtime or poor UX can also be eliminated with proper analysis and data provided by APM monitoring tools.
5. Better collaboration
There are certain organizations in which employees or team members focus solely on their respective objectives rather than organizational goals.
However, when metrics are shared among team members on a collective basis, chances are high that the IT teams will break their silos, collaborate, and perform their best to resolve issues as a team.
Further, working together makes the whole process of achieving organizational goals simple and effective.
6. Proactive Issue Detection
With constant monitoring, developers can find the issues before they impact the performance or escalate into a major issue. The Application Performance Monitoring tool helps find issues in real time and enables teams to take corrective measures for smooth IT operations.
With early detection of issues, businesses can improve their response time and reduce downtime.
How is APM different from observability?
APM and observability are two related concepts in the field of performance monitoring, but they have distinct differences.
While both APM and observability focus on monitoring the performance of software applications, they differ in terms of their scope and approach.
APM primarily focuses on monitoring and managing the performance of applications. It involves the collection of performance data from various sources, such as servers, databases, and network devices, to identify performance bottlenecks and potential issues.
APM provides actionable insights and recommendations for optimizing application performance and enhancing user experience.
On the other hand, observability is a broader concept that encompasses not only performance monitoring but also the ability to understand and debug complex systems.
Observability focuses on the ability to gain insights into the internal workings of a system based on observed data.
It involves collecting and analyzing various types of data, such as logs, metrics, and traces, to gain a comprehensive understanding of system behavior.
While APM provides specific insights into application performance, observability provides a more holistic view of system behavior.
Observability enables organizations to understand how different components of a system interact and identify potential issues that may impact performance.
What are the Use cases of Application Performance Monitoring?
Here are a few use cases of APM software, including:
Real User Monitoring
The collection and analysis of user data to develop a knowledge of an application’s performance levels is known as real user monitoring.
You can precisely forecast when an application will encounter problems by setting a baseline for acceptable performance.
For example, the APM notifies the appropriate teams if the quantity of consumers having trouble checking out their purchases exceeds a predetermined level.
In such a case, either you can perform synthetic monitoring to capture problems before the application goes for production or perform agentless monitoring.
Infrastructure monitoring
Be it virtual machines, servers, databases, or other systems in an IT infrastructure, APM collects all data from different sources and performs analysis to identify application performance issues and faults in an application.
E-commerce websites
Most businesses run e-commerce businesses to sell their products and services to a larger audience and gain good profits. To perform these actions, it relies on applications and its smooth functioning.
APM helps track the overall performance of applications, transactional processes, and other aspects for smooth operations.
Further, it ensures seamless checkout experiences for its users by tracking all the components of an application.
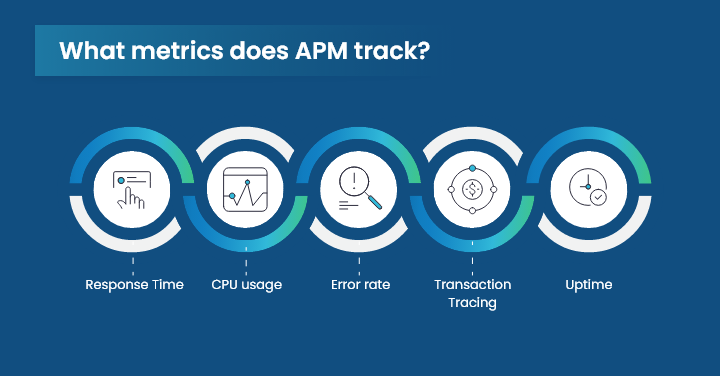
What metrics does application performance monitoring track?
Here are some of the common metrics that a business can monitor using Application Performance Monitoring, including:
- Response Time – Response time is one of the key metrics in a business for it updates how much time it took for a user to respond to the customer’s request. High response time implies that the user responded to the request without any delay, resulting in satisfied customers. These are generally measured by setting a predetermined threshold limit. If the count falls below the set limit, the solution will send an alert to the team and compare performance to an acceptable baseline.
- CPU usage – Another key metric is CPU usage which can be tracked using this powerful software. Be it CPU utilization score or memory usage, the application performance monitoring solution tracks it all and notifies if the program is receiving the processing power it needs to function properly.
- Error rate – With APM, users can run a complete thorough analysis of the modern applications and report error rates. For example, database query failure or inquiry times out. As the error rate goes beyond the set parameter, an alert will be automatically sent to the team updating about the potential future issues.
- Transaction tracing – It provides a precise image of each individual transaction made within an application, i.e., any external call, database call, etc., to keep an update of all the transactions.
- Uptime – This metric is highly crucial for any business that offers online service. Most service level agreements (SLAs), only permit a certain percentage of downtime during predefined intervals. However, with this monitoring tool, you can keep track of application availability and compare it with customer-specified levels.
Advantages of an advanced APM platform
Advanced APM platforms provide several advantages in comparison to the traditional monitoring methods, such as:
1. Advanced cloud observability
AWS, Azure, and GCP are some of the popular cloud platforms used by a large group of businesses. Basically, these applications, which run in containerized environments distributed across different cloud services, are made up of millions of lines of code and feature With the help of APM solutions, businesses can smoothly work on these platforms and gain detailed insights into the operations in the cloud environment.
The best part about these platforms is they do not require any configuration or training as they manage everything on their own and provide complete observability.
Right from tracking down the application performance to keeping a check on component status, everything is possible with the advanced APM platforms.
2. Continuous automation
With continuous automation capabilities, chances of human error will be reduced and all operations will be performed at a faster pace.
Be it automated discovery of components, identification of unusual patterns, or triggering predefined actions, all tasks will be completed quickly and too without the need for manual intervention.
Organizations must constantly automate operations to ensure proper application performance because humans are incapable of maintaining, configuring, scripting, and sourcing data in a cloud-native environment.
Automated processes will save time and human effort, resulting in an overall improvement in performance and customer satisfaction.
3. AI Assistance
The Application Performance Monitoring platforms use AI techniques and algorithms to run proper analysis on the information gathered from different applications.
With the help of AI assistance, users are able to find the root cause of the issue and detect anomalies at an initial stage, enabling quick solutions to the issue before it affects business operations.
Further, AI methods aid teams in prioritizing and filtering alerts based on their impact.
4. Cross-team collaboration
By providing a centralized center where various teams within an organization may collaborate more successfully, advanced APM technologies enable cross-team communication.
These platforms facilitate information sharing, collaborative problem-solving, and goal alignment among teams, regardless of their departments.
Your team members might belong to the operational department or development department, however, with the APM, teams gain a unified view of the overall app performance and related KPIs, resulting in quick solutions and effective decision-making.
Conclusion
There’s a good probability the end user will move to another application if it loads slowly or continuously displays faults on the screen. An application failure can thereby destroy the goodwill of your company.
Therefore, it’s best to spend time and money on top application performance management tools in order to track, manage, assess the performance of your application and deliver better end user experience.
Businesses can maintain system functionality and catastrophe recovery with these potent tools. Your company will be better equipped to identify and track the errors and defects that are interfering with IT operations and negatively affecting your performance with the right insights and reports.
You can further prevent issues more quickly by using APM tools like Motadata and deliver seamless customer experience.
If you want to avoid users having a negative application experience or calling your help desk frequently, it is best to troubleshoot issues using these tools. Its exclusive features help improve performance and optimize code efficiency.
FAQs
With APM, developers can gain full visibility into the different components of applications that help identify problems and errors in the application resulting in downtime.
By identifying the faults at an initial stage and troubleshooting issues, organizations can reduce errors and downtime that impacts directly the user experience.
As a result, the user faces fewer issues operating a software application, i.e., a higher satisfaction level and more revenue returns to the company.
APM uses machine learning and Artificial intelligence methods to trace transactional processes, monitor performance metrics, and detect anomalies.
It collects data from different sources, monitors unusual patterns, and discovers errors in real time.
Also, it plays a crucial role in preventing downtime by finding out and resolving issues that may turn into bigger problems in the future if left unnoticed and impact the application’s performance.
With all these actions, APM helps optimize the performance and improve user experience.
Performance issue diagnosis and resolution are made easier by integrating APM with DevOps methods.
Teams can identify and fix errors and bottlenecks during development by obtaining real-time application performance statistics by integrating effective APM tools into the CI/CD process.
Performance monitoring and enhancement of the application are encouraged by this integration.
APM in DevOps provides:
- Real-time insights into application performance.
- Facilitating rapid issue detection.
- Faster troubleshooting.
- Collaboration between development and operations teams for continuous improvement.