Introduction
In today’s fast-evolving digital landscape, effective IT service management isn’t just an operational necessity—it’s a strategic advantage.
Organizations rely on IT to drive business success, making IT Service Management (ITSM) a critical component in aligning IT services with corporate objectives.
Yet, within the broad realm of ITSM, one framework stands out: ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library). While they are often mentioned together, ITSM and ITIL serve distinct yet complementary roles.
Let’s dive deep into their relationship, explore their differences, and uncover how they work in tandem to elevate IT service delivery.
The Foundations of ITSM and ITIL
To truly grasp the contrast between ITSM and ITIL, it’s essential to define their core functions. IT Service Management (ITSM) is an overarching approach that focuses on delivering and managing IT services efficiently.
It provides a structured methodology to plan, implement, support, and continuously improve IT services, ensuring they align with business goals.
ITIL, on the other hand, is a widely adopted framework within ITSM. It offers a structured set of best practices, guidelines, and processes to enhance IT service management.
Think of ITSM as the philosophy that governs IT services, while ITIL serves as the playbook that provides tactical guidance for executing ITSM effectively.
The Essence of ITSM: A Holistic Approach to IT Services
IT Service Management (ITSM) is more than a set of processes—it’s the backbone of modern IT operations. It integrates people, processes, and technology to ensure IT services run seamlessly, creating value for both businesses and end-users.
The true power of ITSM lies in its adaptability; whether an organization is a small startup or a global enterprise, ITSM provides the framework to ensure IT services are not just operational but strategic.
A strong ITSM foundation enhances service quality, optimizes workflows, and ensures IT resources are leveraged effectively. Frameworks like ITIL provide a structured approach to ITSM, offering a roadmap for continual improvement and sustained business-IT alignment.
ITIL: The Blueprint for Effective IT Service Management
If ITSM is the orchestra, ITIL is the conductor. ITIL provides a comprehensive set of best practices that guide organizations in delivering high-quality IT services while ensuring efficiency, adaptability, and customer satisfaction.
But ITIL is more than a rigid framework—it’s an evolving methodology that adapts to the complexities of the digital world.
The latest iteration, ITIL 4, moves beyond the traditional process-driven approach, embracing flexibility, collaboration, and value co-creation.
ITIL 4 emphasizes a holistic view of IT services, integrating Agile, DevOps, and Lean principles to ensure ITSM remains relevant in today’s fast-paced technological landscape.
By leveraging ITIL’s guiding principles, organizations can implement tested methodologies, establish clear roles and responsibilities, measure service performance, and foster a culture of continuous improvement—all of which contribute to superior IT service management.
The Business Case for ITSM: Why It’s Essential
A well-executed ITSM strategy does more than manage IT services—it transforms them into a competitive advantage. Here’s why ITSM is indispensable:
1. Bridging the Gap Between IT and Business Goals
In a hyper-competitive environment, businesses cannot afford IT operations that function in silos. ITSM facilitates seamless integration between IT services and business objectives, ensuring that every IT initiative supports broader corporate goals.
A key element of ITSM is Service-Level Management (SLM), which defines clear performance benchmarks for IT services. Through structured service-level agreements (SLAs), organizations can measure IT effectiveness, align IT efforts with business expectations, and ultimately drive operational success.
ITSM also fosters a culture of continuous improvement, encouraging organizations to reassess IT performance, incorporate stakeholder feedback, and refine processes to meet evolving business needs.
2. Enhancing Efficiency and Productivity in IT Operations
Efficiency is at the heart of effective IT operations, and ITSM serves as the catalyst for streamlined workflows.
By establishing standardized processes—ranging from incident and change management to problem and knowledge management—ITSM minimizes inefficiencies, reduces redundancies, and ensures IT teams operate at peak performance.
Automation plays a crucial role in ITSM-driven efficiency. By leveraging automation tools to handle routine tasks such as ticket logging, request fulfillment, and incident resolution, IT teams can redirect their focus towards strategic initiatives, proactive problem-solving, and innovation.
With optimized processes and intelligent resource allocation, organizations can improve service responsiveness, reduce downtime, and enhance overall IT performance.
3. Elevating Customer Satisfaction Through Superior Service Delivery
In the digital economy, user experience is paramount. ITSM prioritizes customer-centric service delivery, ensuring that IT services are not only reliable but also tailored to user needs.
By gathering and analyzing user feedback through multiple channels—including service desk interactions, surveys, and real-time monitoring—ITSM enables organizations to continuously refine their IT services.
Transparency and proactive communication further enhance customer satisfaction, as users receive timely updates on service requests, maintenance schedules, and self-service solutions.
When IT services are responsive, efficient, and user-focused, organizations build trust, enhance user engagement, and cultivate long-term customer loyalty.
4. Reducing Costs Through Process Optimization
Cost optimization is a pressing concern for every organization, and ITSM offers a structured approach to maximizing efficiency while minimizing expenses.
By standardizing workflows, automating repetitive tasks, and eliminating inefficiencies, ITSM helps organizations significantly reduce operational costs.
Proactive problem and change management also play a pivotal role in cost reduction. By identifying potential service disruptions before they escalate, organizations can prevent costly downtime, mitigate risks, and maintain business continuity—ensuring a higher return on IT investments.
5. Strengthening Risk Management and Compliance
In an era of increasing cybersecurity threats and regulatory scrutiny, risk management and compliance are non-negotiable. ITSM provides organizations with a robust framework to identify, assess, and mitigate IT-related risks, safeguarding critical business assets and data.
By implementing structured controls for data access, incident management, and security protocols, ITSM enhances organizational resilience.
Regular audits, compliance tracking, and detailed documentation further ensure adherence to regulatory standards, reducing the risk of non-compliance penalties and reputational damage.
6. Driving Service Excellence and Reliability
Excellence in IT service delivery is not a one-time achievement—it’s a continuous pursuit. ITSM serves as a guiding framework that enables organizations to deliver consistent, high-quality IT services while adapting to evolving business needs.
By actively monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) such as service uptime, incident resolution times, and customer satisfaction levels, ITSM provides valuable insights that drive ongoing service improvement.
Through continuous assessment and refinement, organizations can enhance IT reliability, improve service availability, and exceed user expectations.
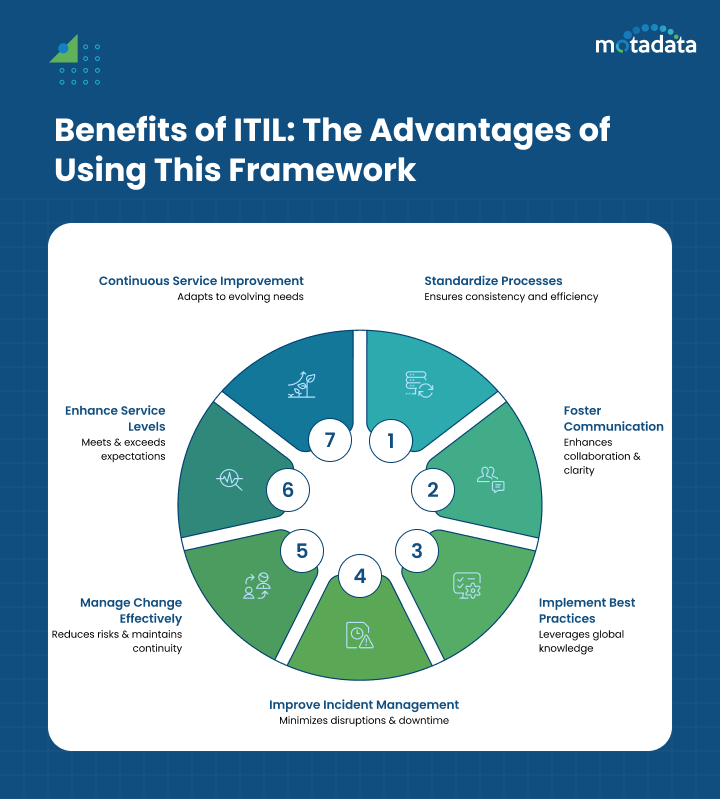
Benefits of ITIL: The Advantages of Using This Framework
IT Service Management (ITSM) provides a structured approach to managing IT services, while ITIL offers a comprehensive framework that helps organizations align their IT operations with business objectives.
With a strong foundation of best practices, ITIL is widely adopted by businesses worldwide to enhance service quality, standardize processes, and drive continuous improvement.
Beyond optimizing IT processes, ITIL fosters a customer-centric IT culture, adding business value and supporting sustainable growth. Let’s explore the key benefits of adopting ITIL.
1. Standardized and Consistent Processes
Consistency is crucial for effective IT service delivery. ITIL provides a well-defined framework that standardizes IT processes, ensuring efficiency, reducing errors, and enhancing the customer experience.
By following a structured approach to incident management, problem resolution, change implementation, and service requests, organizations can minimize miscommunication, delays, and operational risks.
A standardized framework also enables better tracking and performance measurement, allowing IT teams to identify inefficiencies, improve service quality, and demonstrate their value to the business.
2. Common Language and Unified Understanding
Effective communication and collaboration are essential for seamless IT operations. ITIL establishes a common language across IT teams, ensuring clarity and consistency in IT service management.
Without a shared framework, different teams may develop their own terminologies and workflows, leading to confusion and inefficiencies.
ITIL standardizes ITSM terminology, helping service desk agents, IT managers, and other stakeholders work together efficiently.
This shared understanding fosters better collaboration, streamlines issue resolution, and promotes a knowledge-sharing culture within IT teams.
3. Proven Best Practices from Global Experience
ITIL is not just a theoretical framework—it is built on real-world best practices gathered from organizations across various industries.
By adopting ITIL, businesses gain access to a wealth of knowledge, case studies, and strategies that have been successfully implemented worldwide.
This global perspective enables organizations to avoid common pitfalls, accelerate ITSM maturity, and align their IT services with industry standards.
ITIL’s best practices help IT teams stay ahead of evolving trends, ensuring that their IT services remain resilient, adaptable, and competitive in an ever-changing digital landscape.
4. Improved Incident and Problem Management
IT disruptions are inevitable, but how organizations handle them makes all the difference. ITIL provides a structured approach to incident and problem management, minimizing service disruptions and enhancing business productivity.
Through ITIL’s incident management practices, organizations can swiftly detect, classify, prioritize, and resolve incidents, ensuring minimal downtime.
The framework also emphasizes proactive problem management, identifying recurring issues and addressing their root causes to prevent future disruptions.
By analyzing incident patterns and implementing long-term solutions, IT teams can enhance IT stability and ensure seamless service delivery.
5. Better Change Management with Minimal Disruptions
Change is essential for innovation, but it also introduces risks. ITIL’s change management framework helps organizations plan, assess, and implement IT changes while minimizing disruptions to business operations.
By carefully evaluating potential risks before making changes, IT teams can proactively address vulnerabilities and maintain service continuity.
ITIL also promotes transparent communication with stakeholders throughout the change process, ensuring alignment, managing expectations, and reducing resistance to change.
This structured approach enables organizations to embrace transformation without compromising service reliability.
6. Enhanced Service Level Management and Accountability
Meeting and exceeding customer expectations is a top priority for IT service providers.
ITIL’s Service Level Management (SLM) practice ensures transparency, accountability, and continuous service improvement through clearly defined service performance metrics.
Service Level Agreements (SLAs) establish measurable performance benchmarks, such as service availability, response times, and resolution speeds.
Regular reporting and monitoring of these KPIs help IT teams assess their performance, identify areas for improvement, and demonstrate their commitment to delivering value-driven IT services.
7. Continuous Service Improvement for Long-Term Success
The dynamic nature of IT demands continuous evolution. ITIL instills a culture of ongoing service improvement, ensuring that IT services remain agile, efficient, and aligned with business needs.
Through ITIL’s Service Value Chain (SVC) model, organizations can continuously assess service performance, gather stakeholder feedback, and implement iterative improvements.
This proactive approach encourages innovation, fosters learning, and equips IT teams with the agility to respond to emerging business challenges effectively.
By embracing ITIL’s continuous improvement philosophy, organizations can future-proof their IT operations, maintain service excellence, and sustain long-term business growth.
The Relationship in Action: How They Work Together
Think of ITSM as the blueprint for a well-structured house, and ITIL as the bricks, mortar, and tools that bring it to life.
ITIL provides clear processes and best practices that help organizations establish, refine, and optimize ITSM, turning strategic goals into tangible results.
The synergy between ITIL and ITSM enables organizations to build a robust and adaptable ITSM framework tailored to their business needs.
This seamless integration shifts IT service management from a reactive, problem-solving approach to a proactive, customer-centric model.
Ultimately, this collaboration enhances business value and supports key organizational objectives.
Practical Examples of ITIL Processes in ITSM
By leveraging ITIL processes such as incident management and change management, ITSM ensures rapid service restoration and minimal disruptions.
- Incident Management: When an IT issue arises, incident management swiftly classifies, prioritizes, and resolves it, reducing downtime and ensuring business continuity.
- Change Management: By implementing structured change management, IT teams can introduce system modifications in a controlled manner, reducing risks and maintaining service stability.
These ITIL-driven processes not only enhance operational efficiency but also improve customer satisfaction by maintaining high service quality and aligning IT performance with business objectives. The fusion of ITIL methodologies with ITSM practices fosters a culture of continuous improvement, driving sustainable success.
ITIL: A Structured Approach to ITSM Implementation and Enhancement
ITIL offers a well-defined framework for implementing and continuously improving ITSM.
Organizations that follow ITIL’s structured guidelines can systematically enhance IT service quality, align IT operations with business goals, and drive measurable improvements.
By adopting ITIL best practices, businesses gain a strategic roadmap for continuous service improvement, ensuring their IT services evolve in response to dynamic market demands.
This structured approach not only boosts efficiency but also strengthens customer satisfaction, reinforcing IT’s role as a business enabler.
Beyond ITIL: Exploring Other ITSM Frameworks and Methodologies
While ITIL remains the most widely recognized IT Service Management (ITSM) framework, the IT landscape is diverse, requiring organizations to explore additional methodologies to optimize service management.
Frameworks such as COBIT, ISO/IEC 20000, and DevOps provide complementary approaches that enhance IT governance, streamline operations, and improve service delivery.
- COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies): COBIT is designed for IT governance and control, ensuring that IT aligns seamlessly with business objectives. It emphasizes risk management, regulatory compliance, and resource optimization, making it a valuable choice for enterprises that require structured governance over IT services.
- ISO/IEC 20000: As the international standard for IT service management, ISO/IEC 20000 provides benchmarks for service quality, security, and efficiency. Organizations seeking to establish a standardized approach to ITSM while demonstrating compliance with global best practices often adopt this framework.
- DevOps: By bridging the gap between software development and IT operations, DevOps fosters a culture of collaboration, automation, and continuous integration. This approach accelerates software delivery, enhances operational agility, and ensures that IT services are adaptable in fast-changing business environments.
Each of these frameworks addresses specific aspects of ITSM, providing businesses with tailored solutions based on their unique operational requirements.
Expanding ITSM with Alternative Approaches
Beyond ITIL, organizations can leverage other methodologies to refine their IT service management strategy and drive efficiency:
- DevOps fosters a culture where development and operations teams collaborate seamlessly, breaking down traditional silos. By integrating automation, continuous deployment, and feedback loops, DevOps reduces bottlenecks, enhances service agility, and enables organizations to adapt swiftly to market changes.
- Lean IT, inspired by Lean manufacturing principles, focuses on eliminating inefficiencies in IT processes. It identifies and removes non-value-adding activities, streamlining workflows and optimizing resource utilization. This approach is particularly beneficial for organizations looking to enhance productivity and reduce operational costs.
- COBIT, while often associated with IT governance, also plays a crucial role in ITSM by ensuring alignment between IT services and business strategies. It provides structured control mechanisms for risk management, compliance, and performance monitoring, making it ideal for enterprises that prioritize governance and accountability.
By integrating these frameworks into their ITSM strategy, organizations can build a flexible and resilient IT environment that aligns with business goals and evolving market demands.
Choosing the Right ITSM Framework
Selecting the right ITSM framework requires a clear understanding of an organization’s challenges, priorities, and long-term objectives. While ITIL offers a foundational approach, other frameworks can be adopted based on specific needs:
- If slow software development cycles hinder innovation, DevOps can accelerate releases through automation, continuous integration, and enhanced collaboration between development and operations teams.
- If IT processes are inefficient and resource-intensive, Lean IT provides a structured way to optimize workflows, eliminate waste, and improve operational efficiency.
- If governance, risk management, and compliance are top priorities, COBIT ensures regulatory adherence and structured IT management, reducing business risks and enhancing transparency.
Conclusion
Understanding the relationship between ITSM and ITIL is essential for optimizing IT operations.
While ITSM focuses on managing services to meet business objectives, ITIL provides structured processes that improve service efficiency, quality, and alignment with organizational goals.
Integrating ITIL with complementary frameworks like DevOps, Lean IT, and COBIT allows businesses to customize their ITSM strategy for enhanced service delivery and operational excellence.
A tailored, multi-framework approach ensures organizations can adapt to evolving IT landscapes and drive long-term success.
For expert guidance on leveraging ITIL within your ITSM strategy, explore our FAQs below.
FAQs:
Using ITIL in an ITSM strategy brings many benefits. It helps create standard processes to ensure consistency. This leads to lower costs through better use of resources. You also get better service quality, and there is a clear way to keep improving services. All of this works together to increase business value.
ITIL is easy to adapt, which helps businesses of any size. Many people think of ITIL as a tool for big companies. However, its ideas can also be customized for smaller businesses. This helps them improve their IT service management and create more value.
ITIL gets updates from time to time. This helps it stay relevant with new technology and business methods. These updates show that ITIL cares about continual improvement. Using the latest version allows organizations to make use of the most current best practices.
Before adopting ITIL, it’s important to understand your organization’s current ITSM maturity and its business objectives. You should also identify the areas that need improvement. Having a clear ITSM strategy can help you get the most out of ITIL implementation.