Businesses incline toward cloud computing because it offers various benefits, including pay-as-you-go, rapid scaling up, and the ability to utilize resources instantly with downtime.
However, everything we do in the information technology business must address cybersecurity. This blog will cover the influence of the cloud in safeguarding enterprises.
Enterprise cloud security covers the compliance and strategies to protect cloud-based digital assets.
However, cloud computing is complex if you need professional help from a trusted cloud consulting company.
Cloud environments, data kept there, cloud-based apps and people engaging with cloud resources are all protected by enterprise cloud security.
Most cloud arrangements assign different security responsibilities to the cloud provider and the consumer.
What is Enterprise Security
The term “enterprise cloud security” describes the collection of procedures, tools, guidelines, and safeguards businesses implement to protect their information, programs, and hardware when utilizing cloud computing services.
There are several factors to consider when discussing cloud security, including cloud deployment patterns and cloud-shared service models.
But why are organizations switching to cloud computing? “Cloud Computing” describes the rapid use of computing resources, including servers, software, data repositories, networking, development tools, and more.
These resources are housed in remote data centers run by a cloud services provider.
This strategy has numerous benefits, including lower IT expenditures, more effortless resource adjustment based on needs, improved performance, and higher reliability.
Relevance of Enterprise Cloud Security
With the emergence of digital transformation and its rapid adoption, everything has shifted online.
Data became the only asset to protect and operate. Businesses are migrating their data to the cloud, which makes security measures more crucial.
With everything being online, cyber-attacks have increased, and companies are constantly looking for security measures, such as encryption, access controls, monitoring and logging, threat intelligence audits, access limits, and encryption.
Businesses prioritizing data protection can fortify their defenses against attacks and foster stakeholder confidence.
Business Continuity:
Business continuity is necessary for all businesses, and cloud security is essential to keeping operations going.
Effective cloud security policies must include disaster recovery planning, redundancy controls, and data backup to ensure company continuity during unanticipated disruptions.
Multi-tenancy Risk:
Numerous businesses take advantage of multi-tenancy in cloud settings. Nevertheless, this presents unique security issues.
A sophisticated strategy incorporating strong identification and access management mechanisms, encryption, and frequent audits is needed to comprehend and reduce these threats.
How to Improve Enterprise Cloud Security?
There are various ways in which one can improve enterprise cloud security; a few of them are mentioned below:
1. Data Encryption
It is an essential aspect of cloud security. Data encryption protects sensitive information by making it unreadable and restricts access to only authorized people with the necessary decryption keys.
To further secure your cloud-based email communications, businesses should also focus on email authentication by setting up DMARC to prevent email spoofing and phishing attacks.
This does not provide data that is equipped and stored in an administrative setting. The cloud is not compromised or accessed by unauthorized users.
2. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
For cloud security, IAM is very essential. Preventing unauthorized access ensures that authorized users have access to appropriate resources. Ensuring that only verified identities interact with sensitive data requires a reliable identity checking process to confirm users before granting access to enterprise systems.
IAM establishes user lists, monitors their transactions, and implements a strict authentication scheme.
This involves sensitive data protection, compliance management, and neutralizing threats.
Cloud computing reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized system access as it has effective identity and access management.
3. Network Security
Because network security creates the pathways for data to and from the cloud environment, it is essential to enterprise cloud security.
Intrusion detection systems, firewalls, encryption protocols, and access controls prevent cyber attacks and unauthorized access and contain data breaches through solid network security.
Ensuring data confidentiality, integrity, and availability is essential to systematically maintaining the overall reliability, compliance, and security of an organization’s cloud.
4. SIEM
A solution that integrates and analyzes log data from multiple sources to identify threats and immediately respond to problems, SIEM systems support all levels of security in a cloud infrastructure through their eyes for monitoring cloud activity, detecting anomalies, and providing insights into potential vulnerabilities.
5. DLP
Data loss prevention, or DLP, is a component of enterprise cloud security that uses laws and technology to prevent sensitive information from being disclosed or shared without consent.
It monitors data flows, enforces policies, sounds warnings, or takes appropriate action when potential breaches are detected to guarantee that data in cloud settings is secure and compliant.
6. Patch Management
Patch management is essential for enterprise cloud security. It comprises regularly applying security updates and software to systems, applications, and infrastructure.
Keeping all components current helps organizations reduce the risk of breaches, fix known vulnerabilities, and ensure a secure and robust cloud environment. Along with patching known issues, organizations should also rely on static application security testing tools to detect vulnerabilities early in the development cycle, strengthening overall cloud security.
Read Also: How to Ensure Patch Compliance
7. Governance and Compliance
Cloud security governance and compliance are all about creating policies, procedures, and frameworks to ensure that industry regulations and internal standards are adhered to.
This means conducting regular audits, monitoring and enforcing security measures, and synchronizing security protocols with legal requirements.
It ensures that cloud operations uphold security requirements, minimize risks, and preserve transparency to safeguard data, privacy, and the overall integrity of the business.
8. Zero Trust Implementation
Ensuring cloud security for a company requires the use of Zero Trust. The notion that no one can be automatically trusted, inside or outside the network, replaces the traditional ” trust but verify” approach.
Every person and every device needs to authenticate and validate before they may access resources continuously.
This idea is crucial to modern cybersecurity methods because it increases data safety in cloud environments by reducing the attack surface, preventing lateral movement, and lowering the impact of breaches.
5 Must Things You Should Know About Enterprise Cloud Security
Three key deployment strategies must be considered when choosing a cloud. These three sorts of clouds are public, private, and hybrid.
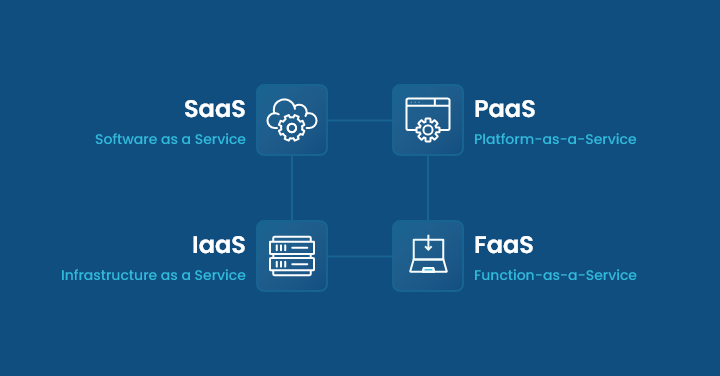
Additionally, most frequently used phrases like Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) differentiate with each having particular advantages.
The risk involved ultimately dictates the most advantageous company approach for you.
The following five points should be known to you, regardless of the model you are deploying to:
1. Data Encryption while Transmission and at Rest
All data, whether in transit over the internet or at rest, should be encrypted by your service provider.
Knowing the essential security precautions becomes vital because you will access all the data from a distance.
Furthermore, authorized corporate resources should only read a service provider’s program when it arrives in your system.
Additionally, find out what kind of encryption is applied to the data in your organization.
2. Shared Resources
Multi-tenancy refers to the shared resources your cloud service provider will allocate to your data.
Virtual servers share resources on the same machine as containers rather than being separate physical infrastructures dedicated to a specific business or application.
This is how virtualization and the cloud work. It is crucial to ensure that the cloud service provider protects your containers and prevents illegal access to your data.
3. Centralized Visibility for Cloud Infrastructure
More than allocating and entrusting everything to service providers is required. Additionally, we need to confirm that the host’s host’s environment is secure for the data.
Tools for cloud workload protection give you consolidated visibility over all of your data so you can see everything at a glance.
Additionally, determine if the service provider provides vulnerability warnings, network traffic analysis, cloud environment inspection, container monitoring, and configuration.
4. Threat Intelligence with Vendor Prawl Management
There will be several providers for intricate cloud installations, each with its unique cybersecurity framework. Using threat intelligence solutions, you may get accurate information on your vendors and local and international risks.
These technologies provide you with global cybersecurity data and help you identify threats and weaknesses.
5. Secure and Integrated Access Model
Access control techniques in cloud systems continue to be a significant issue. User Identity and Access Management (IAM) prevents abuse of privileged accounts.
Cloud-based security, which includes a management system for assigning and removing user roles and access credentials, should be provided by your service provider.
In addition to having an automated revocation procedure in the event of unusual activity, the solution should alert you to any unknown access requests.
Conclusion
Enterprise cloud security helps firms stay ahead of the curve as they migrate to the cloud by providing flexible and dependable solutions.
You must collaborate with a cloud consulting company as they are highly efficient with advance technology.
During this procedure, they prioritize safety by employing data encryption techniques and utilizing Cloud Profiles, which include all required configurations for the specific cloud being used, such as security groups and subnets.
Their dynamic scaling capability is essential for effectively managing cloud hosting deployments for businesses expanding quickly.
This enables to efficiently address the changing requirements of growing companies as they move toward utilizing cloud computing.
FAQs
Cloud computing provides enterprises with scalable, flexible, and cost-effective IT infrastructure and services. Its strategic significance lies in enhancing agility, enabling innovation, and optimizing resource utilization, ultimately safeguarding the future competitiveness of enterprises.
Cloud services provide robust backup and disaster recovery solutions. Enterprises can replicate data across geographically dispersed data centers, ensuring data resilience and minimizing downtime in the event of disruptions or disasters.