Remember the MOVEit file transfer vulnerability that became the talk of the town in 2023? It was a high-profile cybersecurity incident that affected over 2,500 organizations and compromised the personal data of more than 66.4 million individuals worldwide.
Organizations that used the MOVEit app suffered data breaches due to an unpatched vulnerability.
It is these incidents that demonstrate why patching known vulnerabilities is essential, or else failed patches can have severe consequences.
In modern Cybersecurity and IT operations, patch management cannot be ignored or taken for granted.
It is a core component that ensures each system remains secure and compliant by addressing bugs and security vulnerabilities early.
Fixing vulnerabilities, applying timely software updates, and ensuring resilience in the enterprise are now primary goals in this changing global market.
With the advancement of technology and dependency on distributed, cloud-native, and hybrid environments, patching has become more complex and critical.
Threat actors are constantly evolving and adapting new techniques to breach your data.
Zero-day exploits and supply chain vulnerabilities are becoming more common.
On the other hand, IT environments are also expanding their boundaries and moving to IoT and operational technology (OT) domains.
With both attackers and businesses working on developing their area, it has become essential to implement patch management strategies that are more proactive and risk-aware.
These trends are essential for avoiding emerging threats and maintaining a resilient IT infrastructure. In this blog, we will list some of the top patch management trends for 2026.
Top Patch Management Trends Expected in 2026
Cybercriminals are using AI-driven approaches to bypass traditional defenses. Some even use unsecured networks and weak endpoints to expose business data.
The lack of adequate security features is the biggest drawback for most businesses and one of the significant reasons behind data breaches.
Hence, to stay protected in 2026, companies must invest in proactive strategies and predictive patching.
Here are a few patch trends that will be introduced into flexible systems to meet these challenges.
With these trends in practice, organizations can focus more on other areas.
These changes will automatically help businesses protect sensitive data, reduce risk, and improve their security posture.
Trend 1: The Rise of Predictive Patching with AI and Machine Learning:
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are now being leveraged in patch management systems to predict security vulnerabilities and potential threats in advance.
This transformation from reactive to predictive patching completely changes the game for businesses.
Rather than waiting for security patch release or vulnerability exploitation, this new approach will help analyze multiple data sources and detect deviations early.
Besides automation, implementing AI/ML algorithms in patch management offers various benefits.
Implementing these sophisticated tools will allow IT managers and experts to analyze historical exploit patterns and user behavior faster.
Also, Natural language processing (NLP) is being used to scan threat intelligence reports and identify emerging threats before they impact.
For example, predictive patching algorithms can assess the chances of exploitation and promptly recommend patch deployment across assets at a higher risk.
With these insights, team members can minimize the window of exposure and enhance the effectiveness of patch management.
Trend 2: Intelligent Automation and Orchestration Across Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Environments:
Today, businesses run their applications across different IT environments, including on-premise infrastructure, private clouds, public clouds, etc.
Patch management across these diverse and fragmented IT environments was impossible with traditional manual practices.
However, with intelligent automation on the rise, we can bridge this gap and orchestrate the entire patch lifecycle across multi-cloud environments.
Thus, it makes detecting vulnerabilities easier and allows patch testing and validation.
Further, incorporating these orchestration capabilities helps reduce downtime and ensure consistency across all platforms.
Various patch management software with these features are available in the market.
These tools enable seamless patching at scale, such as Motadata Patch Manager, Microsoft Azure Update Manager, AWS Systems Manager Patch Manager, and Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform.
Cloud-native patching presents unique challenges due to dynamic and distributed cloud environments.
Traditional patching tools often struggle with short-lived containers, serverless functions, and autoscaling instances.
However, organizations can use any of these tools to ensure that cloud-native environments receive timely patches without disrupting workflows.
Trend 3: Context-Aware and Risk-Based Vulnerability Management (RBVM) 2.0:
Managing patches using a traditional approach usually involves CVSS scores to prioritize patches. However, not all vulnerabilities pose the same level of risk to every organization.
It is time to shift from the basic CVSS scores approach to the Risk-Based Vulnerability Management (RBVM) 2.0 approach.
By implementing this new approach, security teams can focus on critical vulnerabilities and free themselves from the mindset of patching everything.
Many organizations have already started incorporating business context, asset criticality, and real-time threat intelligence into their patching strategies.
For example, a business encountered known security vulnerabilities in two devices – an online payment system for customers and an internal tool used by a few employees.
Even though both showed the same CVSS score, the online payment system fix is more important as it is public-facing and deals with customers’ sensitive data.
On the other hand, the internal tool is less exposed to the internet and has no sensitive data.
Hence, a customer-facing payment system vulnerability is patched faster than the one in the internal tool.
Tenable, Qualys, and Rapid7 InsightVM are trusted threat intelligence platforms and vulnerability scoring systems that can help patch decisions and reduce security gaps.
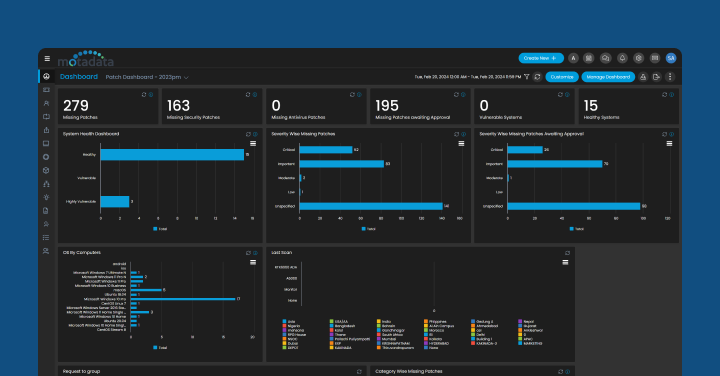
Trend 4: Enhanced Visibility, Granular Reporting, and Actionable Insights:
As patch management becomes more complex, real-time visibility has become more important for modern organizations.
Many businesses are demanding real-time dashboards and advanced analytics that offer a comprehensive view of patch compliance and vulnerability exposure.
These dashboards also highlight trends and anomalies and display insights on missing patches.
Granular reporting tools further allow security teams to generate actionable insights about the software for different team members, system administrators, and stakeholders.
Thus, it is easier to spot unpatched vulnerabilities and misconfigurations.
The reports even share actionable steps for remediation and risk reduction.
Trend 5: Securing the Extended Enterprise: Patching IoT, OT, and Edge Devices:
In recent years, there has been a big increase in the use of IoT devices, edge computing, and operational technology (OT).
These nontraditional systems are often resource-constrained and lack patch management but are deployed in some important places like factories and healthcare centers.
Patching them like normal systems can be a big challenge as most do not have built-in tools for updates.
You need to take them offline to fix them, which can cause workflow disruption.
Companies use new patching strategies, like micro-patching and virtual patching, to avoid this.
Specialized tools like Microsoft Defender for IoT are also used, as they offer more visibility into connected devices and automate patch workflows that benefit these devices.
Trend 6: The Convergence of Patch Management with XDR (Extended Detection and Response):
Patch management has become an important part of security platforms, so security professionals are integrating it with XDR platforms.
The integration mainly aims to improve threat detection, correlation, and response. With this integration, security teams gain more visibility across IT environments and can quickly deploy patches to identify threats.
XDR systems usually collect telemetry from endpoints, networks, and threat intelligence sources.
When patch status is integrated, they can correlate known vulnerabilities with suspicious activity and initiate remediations—further allowing team members to spot unpatched software vulnerabilities earlier.
Trend 7: Embracing “Patch as Code” and Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) Principles:
DevOps teams are increasingly managing infrastructure through code.
Patch trends are expected to extend with “Patch as Code.” Soon, organizations will define patching workflows in code and store them in version-controlled repositories, thus enabling consistency, repeatability, and version control for patching.
As businesses face increasingly complex threats, this strategy will help them avoid security vulnerabilities. It will also ensure that software updates are regularly applied.
IT teams can automate patch deployment during infrastructure provisioning using tools like Terraform and Ansible. Thus reducing configuration drift and enabling faster remediation.
Trend 8: Improved Communication and Collaboration Between Security and IT Operations:
Maintaining a proper connection between security and the IT operations team is vital for improved patch management.
Security teams play a key role in identifying vulnerabilities, but patch deployment is often delayed due to downtime or application compatibility issues.
As software vulnerabilities increase, good communication has become more important. So, this year, organizations are prioritizing collaboration.
Tools like ServiceNow, Jira, and Splunk can be used for smooth communication between both teams.
With proper collaboration, organizations can prepare for upcoming patches and reduce the time to remediate.
Thus, not only improves the process of vulnerability management easier but also strengthens security posture.
Trend 9: The Growing Role of Patch Management in Achieving and Maintaining Regulatory Compliance:
With cybercrime on the rise, governments and industry groups are working towards creating more strict rules and frameworks for data protection.
Frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, etc., will play a key role in timely vulnerability remediation.
If companies don’t patch their systems on time, they might need to pay hefty fines or face legal consequences.
Many companies are viewing good patch deployment with regulatory requirements to ensure compliance.
This trend will further strengthen the overall security posture and boost credibility in the market.
You can use audit logs and real-time compliance dashboards to show adherence to regulatory mandates.
Trend 10: Proactive Vulnerability Disclosure and the Importance of Timely Vendor Patches:
Nowadays, companies do not prefer waiting for months for software updates.
Instead, they expect software vendors to release patches when vulnerabilities are discovered.
Many vendors are adopting proactive vulnerability disclosure policies and faster patch release cycles to meet these demands.
Security professionals see that passing information about these vulnerabilities in a good way can reduce the attack surface. Thus further allowing organizations to stay ahead of threat actors.
Some vendors are joining coordinated vulnerability disclosure (CVD) programs to address issues before public disclosure.
Staying updated can help IT teams respond swiftly and reduce risk exposure.
Navigating the Future of Patch Management: Key Takeaways for 2026
Patch management in 2026 will be defined by new technologies like AI, intelligent automation, collaboration, and predictive analytics.
These tools will make it easier to find and fix vulnerabilities early.
Remember, a proactive, holistic approach that combines technology, processes, and teamwork is essential for staying secure and resilient in the coming future.
Here are a few key takeaways:
- Leveraging AI and machine learning in patch management will help predict and prioritize high-risk vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
- Automating patch workflows across hybrid and multi-cloud environments with orchestration tools is essential, as it minimizes manual effort and prevents human error.
- Adopting a risk-based vulnerability management (RBVM) approach to patching will help consider aspects other than basic CVSS scores, including business context, asset criticality, and real-time threat intelligence.
- Patch visibility and reporting improve with dashboards and analytics that go beyond compliance to provide actionable insights.
- IoT, OT, and edge devices are critical and require specialized solutions like micro-patching and virtual patching to secure the extended enterprise.
- Integrating patching with XDR and security operations ensures that patching supports faster threat detection, response, and correlation.
- Implementing “Patch as Code” and IaC practices will bring consistency and control into DevOps-driven environments.
- Break down silos between teams through shared tools, communication channels, and performance metrics. Stronger collaboration will ensure more effective patching.
- Regulatory compliance is increasingly tied to timely patching, making audit trails and automated documentation important.
- Staying updated with vendor advisories and using threat feeds to respond to critical updates as they are released.
Conclusion
Be it 2026 or the coming years; it is quite clear that effective patch management is not just a practice but a necessity to overcome cybersecurity challenges.
In this digital world, many sources have become available for hackers or threat actors to enter your system.
Cyber threats is growing in volume and complexity. Having an unpatched vulnerability is one of the easiest ways to make entries and exploit data.
Whether it’s a ransomware outbreak or a data breach stemming from a delayed security update, the consequences of poor patching can be severe.
Over the years, patch management has evolved from a regular technical maintenance task into a strategic defense mechanism.
From threat detection and risk mitigation to compliance and business continuity, it is incorporated adequately for your system data security.
Traditional practices are no longer enough to handle complex cyber threats.
The trends shaping patch management in 2026—such as AI-driven vulnerability prioritization, intelligent automation, risk-based strategies, and real-time reporting—offer organizations the tools and insights they need to stay ahead of threats.
You can invest in our Patch Manager Software with advanced features and capabilities.
Businesses can use these patch trends to manage their distributed assets better and reduce risk or downtime.
Embracing these trends will further enable IT managers to shift from a reactive to a proactive patch management approach.
Context-aware vulnerability management, real-time dashboards, compliance reporting, and integration with XDR and security operations are a few patch trends listed above.
Suppose your organization is investing in modernizing its patch management practices.
In that case, there is a high chance that you will better handle emerging threats, maintain compliance, and ensure the resilience of its IT infrastructure.
Check to see if your organization is leveraging the latest tools and insights. Are your teams aligned and collaborating? Share your experiences, challenges, or strategies in the comments below.
Our team would love to hear from you and respond with appropriate solutions to stay secure in 2026.