An asset is any hardware or software contributing value to an organization’s goals, even if it caters to the target audience’s needs. And each asset has its lifecycle that needs to be taken care of.
According to a recent survey, 70% of firms are becoming more interested in integrating ITAM and service desk.
Hence, the first step here is to know how crucial it is to manage the IT asset’s lifecycle effectively.
The asset management system involves a strategic approach to optimize each stage of an asset’s journey—from procurement through deployment, maintenance, asset inventory, and upgrades to eventual disposal.
A well-organized IT Asset Lifecycle Management (ITALM) ensures:
- Resources are utilized efficiently
- The lifespan of the asset is elevated
- Workload is reduced through automation and the use of the right tools
- Costs are minimized through informed budgeting and forecasting
- Compliance with legal and regulatory requirements is maintained
- All the asset details are maintained centrally to minimize data loss
Thus, organizations can enhance productivity, have better ROI, reduce expenses, and ensure adherence to standards in the IT systems by tracking and managing assets throughout their lifecycle, ultimately supporting their broader strategic objectives.
What is IT Asset Management?
IT asset management (ITAM) encompasses the processes, frameworks, and best practices and provides a comprehensive view and analysis for better asset management.
Businesses employ this to oversee and control the lifecycle of their IT assets, address their tangible, monetary, and contractual aspects, and reduce inherent risks.
Some ITAM best practices that an organization must follow to systematize operations, enhance efficiency, and have a better assumption of risk include:
ITAM Best Practices
1. Install Efficient and Comprehensive IT Asset Management Software:
The first stage is to opt for IT asset management software that seamlessly oversees and coordinates all your software and hardware assets.
This should be done from a single, centralized hub. This approach ensures that all the asset-related data is consolidated in one place. Thus providing a complete view of the organization’s assets.
The IT service desk should facilitate smooth management throughout the asset lifecycle, from acquisition and deployment to maintenance and disposal.
Organizations can improve accuracy, enhance visibility, and streamline processes by centralizing asset management and providing more value to the end users.
This leads to better decision-making, reduced cost, optimized asset utilization and a curtailed negative impact on the overall branding.
Additionally, centralized management simplifies compliance tracking and reporting.
This ensures adherence to industry standards and regulations. Lastly, to enhance brand identity, an AI logo creator can quickly generate customized logos that align with the company’s values, ensuring consistency across all assets.
2. Customizable Software:
Customization and sustainability are the key factors to that will keep an IT Asset Management afloat.
Therefore, select an ITAM software that can be customized per the organization’s needs and workflows. Customizability ensures that the software aligns with your unique operational requirements.
For example, the ability to customize fields, forms, and dashboards allows you to track and manage assets in a way that best fits your business processes.
This flexibility extends to workflow automation, where you can create bespoke workflows that mirror your organization’s procedures. Also, this approach streamlines operations and improves efficiency.
Customizable reporting features enable you to generate reports focusing on the metrics most relevant to your goals.
Additionally, you can tailor the user roles and permissions to match your organizational hierarchy.
This confirms that the right people have access to the correct information.
Implementing a highly customizable ITAM allows you to adapt the system to support evolving business needs and improve user adoption.
3. Possess Easy-to-Use Interface:
The IT Asset Management (ITAM) software must have a user-friendly interface that can be adopted quickly. A well-designed interface is intuitive and easy to navigate.
This reduces the learning curve and minimizes the need for extensive training. Moreover, this ease of use encourages regular engagement, keeping the asset data accurate and up-to-date.
Clear menus and straightforward workflows help users to find information and perform tasks efficiently and quickly.
An easy-to-access interface improves compliance with the ITAM processes, as employees are more likely to follow protocols consistently.
Ultimately, it makes the software reachable and enjoyable, boosting the overall IT asset management effectiveness.
4. Automate the IT Asset Management Lifecycle Processes:
Automation is the solution to most of the time-consuming processes. Hence, when the IT management processes are automatized, wonders can occur.
By automating the IT management processes, organizations can achieve remarkable improvements in productivity and accuracy.
For example, robust workflows can automatically update asset properties based on specific events. This ensures the availability of the latest information without any manual intervention.
Additionally, the system can generate detailed reports and promptly notify the relevant recipients about critical events, such as maintenance schedules, compliance deadlines, or security alerts.
This proactive approach minimizes downtime and enhances decision-making by providing on-time and accurate data.
Overall, automation streamlines operations reduces human error and allows IT staff to focus on more strategic tasks. This ultimately results in enhanced productivity and performance in IT management.
5. Regular Status Checkup of IT Asset Lifecycle:
Regularly checking the status of the IT asset lifecycle is essential for maintaining optimal performance and efficiency.
This process involves consistently monitoring each stage of an asset’s lifecycle, which includes purchase, deployment, maintenance, and eventual retirement or removal. Conducting regular checks helps to identify potential issues early.
This proactive approach prevents disruptions that could impact operations. It also ensures that assets are used effectively throughout their lifespan.
Additionally, regular monitoring supports compliance with regulatory standards and industry best practices, reducing the risk of legal or financial penalties.
Ultimately, consistent lifecycle management enhances asset longevity and contributes to overall organizational success.
6. Centralize Asset Repository:
A central asset repository consolidates all IT asset data into a cohesive database, creating a unified view of hardware, software, and licenses.
This centralized system enhances transparency by providing a clear and full perspective on all the assets. It improves accessibility, allowing IT teams to retrieve and manage data from one location easily.
The streamlined setup facilitates more efficient audits and quicker report generation, as all the relevant information is readily available.
Using a central repository makes decision-making more informed, as it provides accurate and inclusive data.
Eliminating data redundancies reduces the risk of inconsistencies and errors, which can lead to costly mistakes.
Additionally, the repository helps to ensure compliance with regulatory standards and industry best practices.
The central repository supports more competent, organized, and cost-effective operations by centralizing asset management and simplifying the IT processes.
7. Asset Reporting and Analytics:
Use extensive reporting and analytic features within your IT asset management (ITAM) software to obtain critical insights about your assets.
Through in-depth reporting, you can track assets and get a clear view of how they are being used across the organization.
This helps identify underutilized assets, which can then be redeployed or retired to optimize resource allocation.
Analytics features enable you to monitor the lifecycle status of assets, from procurement to IT asset disposition.
Analyzing this data lets you predict when assets will require maintenance or replacement. This enables proactive management and reduces unexpected downtime.
Financial metrics are also an integral part of ITAM reporting and analytics.
These metrics help understand the total cost of ownership (TCO) of assets, budgeting for future purchases, and justifying expenditures to stakeholders.
By having a clear financial overview, organizations can make more mindful decisions regarding investments in IT assets.
Detailed reporting and analytics also support compliance with regulatory standards by providing necessary documentation and insights.
In addition to these factors, managing the IT asset lifecycles effectively demands a thorough approach.
This involves meticulously addressing each stage of an asset’s life, starting with acquisition and deployment, then ongoing maintenance, eventually leading to retirement or disposal.
At the acquisition stage, you must verify that you select assets based on current and future needs.
You should consider factors like scalability, compatibility, and cost-effectiveness for this purpose.
During deployment, you need to plan and execute the integration of new assets into the existing IT infrastructure.
Maintenance involves regular monitoring, updates, and repairs to keep the assets functioning optimally and extend their useful life.
This stage also ensures compliance with relevant standards and regulations. When assets reach the end of their useful life, the retirement phase should be handled responsibly, considering data security and environmental impact.
Moreover, continuous improvement is central to this entire process. Regularly reviewing and refining asset management practices based on performance data and new technologies optimizes lifecycle management strategy.
By adopting a proactive and detailed approach, organizations can maximize the value of their IT assets, reduce their costs, and improve overall operational efficiency.
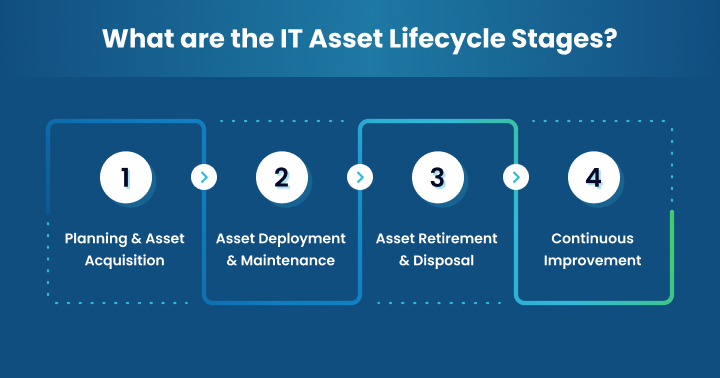
What are the IT Asset Lifecycle Stages?
The IT Asset Lifecycle includes acquisition, deployment, maintenance, and disposal stages.
Effective management ensures optimal performance, cost efficiency, and compliance throughout the asset’s life, supporting the organization’s technological and operational needs.
1. Planning and Asset Acquisition:
Acquiring new IT assets marks the beginning of the lifecycle management process. Organizations must conduct a thorough needs assessment to ensure a smooth start.
This step is vital for making well-informed purchasing decisions. Next, evaluate the potential assets for their compatibility with existing systems.
It is also important to consider how these assets will scale. Establishing clear procurement policies and criteria will help the assets meet organizational requirements and budget constraints.
Effective vendor management is another key element of successful asset acquisition. Building solid relationships with reputable vendors can lead to better terms and conditions.
Clear communication channels are crucial for maintaining a good working relationship.
Additionally, regularly evaluating vendor performance helps suppliers meet quality standards and deliver assets on time.
By following these best practices, organizations can effectively manage their IT assets from acquisition to retirement.
2. Asset Deployment and Maintenance:
Deploying IT assets efficiently requires a well-designed and strategic approach.
Organizations should develop a detailed deployment plan outlining the timelines, roles, and responsibilities.
Training staff on new assets is crucial. Also, the new assets must be compatible with the existing infrastructure for a successful deployment.
Once the assets are deployed, regular maintenance and timely updates are pivotal for their performance and security.
Organizations should establish maintenance schedules and conduct routine inspections.
Applying software updates and patches as needed helps maintain optimal performance.
Proactive maintenance is the key. It helps prevent unexpected failures and extends the lifespan of IT assets.
3. Asset Retirement and Disposal:
Asset retirement or disposal procedures should be proper and responsible. Appropriate retirement measures must be taken when IT assets end their useful life. This ensures data security and regulatory compliance.
The organizations should adopt standardized processes for asset neutralization. This includes thorough data wiping, secure backup, and comprehensive documentation.
Clear guidelines for asset disposal are necessary to mitigate risks. Practical clearance steps help to prevent data breaches and unauthorized access.
Thus, following these best practices, you can safeguard sensitive information and maintain compliance and data integrity.
Along with this, one must also ensure eco-friendly disposal methods are used.
This prevents the environment from any damage. Eco-conscious disposal methods are increasingly important for reducing environmental impact.
Organizations should prioritize eco-friendly practices such as recycling, refurbishing, or donating retired assets.
You can also collaborate with certified e-waste recyclers. They handle these hazardous materials responsibly and comply with environmental regulations.
4. Continuous Improvement:
Continuous monitoring and regular reviews of asset lifecycle processes are key to identifying areas for improvement.
Organizations should track Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), gather stakeholder feedback, and conduct periodic audits.
Monitoring helps to ensure that lifecycle management practices remain effective and aligned with organizational goals.
Implementing continuous improvements starts with analyzing performance data, identifying trends, and making informed process adjustments.
Organizations should foster a culture of continuous improvement by encouraging innovation, providing training, and leveraging technology.
Continuous improvement initiatives help organizations stay agile and enable companies to respond effectively to changing needs.
Conclusion
Thus, after going through what asset management is, knowing its best practices, and the stages involved, I am sure you now understand how a perfect IT Asset Lifecycle Management enables you to step ahead toward the sky of success.
In the market, many organizations provide robust IT Asset Lifecycle Management tools. But which one suits your business is a big question. No worries, here we are to sort that out.
Motadata’s ITAM solution is a powerful tool for managing IT assets throughout their lifecycle.
With features like advanced asset location and movement tracking, software metering, automated processes, insightful reporting, and many more, Motadata helps organizations make informed decisions, enhance efficiency, and achieve their strategic goals.
Choosing Motadata’s ITAM solution means investing in a smarter and more sustainable approach to IT asset management.
This keeps your organization agile and competitive in a rapidly evolving technological landscape.
FAQs:
ITAM is a process for managing IT assets throughout their entire lifecycle to maximize their value and minimize costs.
Improved cost management, enhanced asset utilization, reduced risk, and improved decision-making.
ITAM helps ensure that assets are properly managed, secured, and disposed of, reducing security risks and ensuring compliance with regulations.