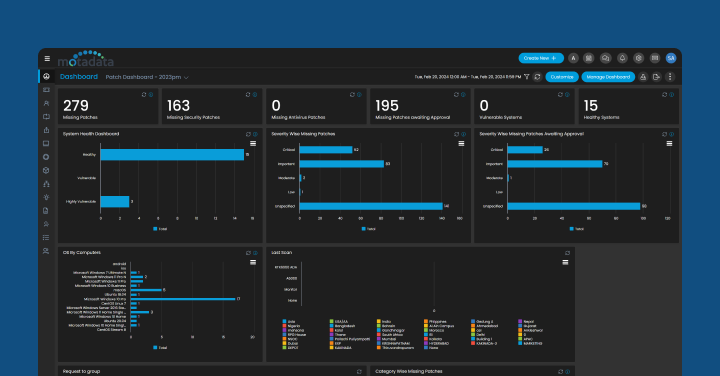
Introduction
Technology has become the backbone of every modern business. Whether you are running a small company or a global enterprise, your operations depend on servers, applications, and endpoints that must always stay secure and available.
In today’s world, IT teams are no longer working with a single environment. Instead, most organizations have adopted a hybrid setup that combines on-premises infrastructure, cloud platforms, and remote devices. While this model is flexible and scalable, it also brings challenges when it comes to security.
One of the biggest responsibilities for IT teams is keeping systems updated. Patches are not just optional fixes; they are critical updates that close security gaps, improve system stability, and ensure compliance with industry regulations. Unfortunately, many businesses still struggle with patch management.
According to Ponemon Institute, 57 percent of data breaches are linked to vulnerabilities that could have been avoided through timely patching. This statistic highlights how crucial it is to have a strong patch management process in place, particularly for Windows systems, which form the backbone of most enterprise environments.
The solution lies in automation. Manual patching may work for a handful of machines, but when you are dealing with thousands of devices across different locations, it quickly becomes inefficient and error-prone.
Automating windows patch management not only saves time but also improves security and consistency across your hybrid infrastructure.
Patch Management in Hybrid Environments
At its core, patch management is the process of identifying, acquiring, testing, and deploying software updates. While the definition sounds simple, the reality in hybrid environments is far from easy.
An organization might have:
- On-premises servers running business-critical applications.
- Cloud workloads hosted on platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
- Hundreds of remote endpoints used by employees working from different regions.
Each of these environments requires patches, but they may follow different processes, schedules, and risks.
A Windows server running in the data center may need patches that are different from those required by a cloud-based virtual machine or a laptop used by a remote worker. Keeping track of these variations manually can feel like trying to plug holes in a sinking ship.
The real challenge is not just applying patches but ensuring consistency across all environments. If even one device is missed, it can become a weak point that attackers exploit.
That is why many IT leaders emphasize automation. Instead of relying on people to keep track of updates, automated systems can handle patch discovery, prioritization, and deployment in a way that is fast and reliable.
Why Automation Matters for Windows Systems
Windows is one of the most widely used operating systems in the world, both for servers and endpoints. Microsoft releases updates on a regular basis, including the well-known “Patch Tuesday” cycle. While these updates are critical, they can also be overwhelming for IT teams who are responsible for hundreds or thousands of devices.
Manual patching in such environments has several drawbacks:
- It takes too much time to identify and apply patches.</li
- Human error is common, leading to inconsistent patch coverage.
- Teams often delay patches to avoid downtime, leaving systems vulnerable.
Automating windows patch management addresses these issues directly. An automated system can scan the environment for missing patches, prioritize them based on severity, and deploy them according to predefined policies.
For example, critical security patches can be applied immediately, while less urgent updates can be scheduled during off-peak hours to avoid disrupting business operations.
This approach not only improves efficiency but also strengthens the security posture of the organization. Automation ensures that no system is left behind, reducing the likelihood of breaches caused by outdated software.
Challenges of Hybrid Setups
Hybrid IT environments are becoming the standard, but they come with their own unique challenges for patch management.
1. Diverse infrastructure
Managing patches across different platforms requires a unified approach. A patching strategy that works for on-premises servers may not be suitable for cloud workloads or remote laptops.
2. Scalability
As businesses grow, the number of devices and applications increases. Scaling manual processes is nearly impossible, which leads to delays and gaps.
3. Security risks
Every unpatched device becomes a potential entry point for attackers. In hybrid environments where visibility is often fragmented, this risk multiplies.
4. Compliance requirements
Industries such as healthcare, finance, and government have strict compliance regulations. Falling behind on patch management can result not only in security risks but also in legal and financial penalties.
These challenges show why automation is no longer a luxury but a necessity for organizations operating in hybrid environments.
Components of a Hybrid Environment
To understand why automation is so critical, it helps to look at the typical components of a hybrid setup.
- On-Premises Infrastructure: These are traditional servers and systems located within the company’s data centers. They often run mission-critical applications and may include legacy systems that are difficult to patch.
- Cloud Workloads: Applications and services hosted in the cloud provide flexibility and scalability, but they require careful patch management to remain secure.
- Remote Endpoints: With the rise of remote and hybrid work, employees are connecting from different devices and locations. These endpoints are often the most vulnerable part of the environment if not patched consistently.
The complexity of managing these different elements highlights the importance of a unified patch management strategy. Automation ensures that all systems, regardless of location, receive the necessary updates without relying on manual intervention.
Benefits of Automating Windows Patch Management
Automation delivers multiple benefits for organizations managing hybrid environments.
1. Time and resource efficiency
Instead of spending countless hours applying patches manually, IT teams can rely on automation to handle the bulk of the work. This frees up time for more strategic initiatives.
2. Improved security posture
Automated systems can apply patches quickly and consistently, reducing the window of opportunity for attackers. This is critical given how quickly new vulnerabilities are exploited.
3. Consistency across environments
Automation ensures that every device, whether on-premises, in the cloud, or remote, receives the same level of attention. This consistency is difficult to achieve with manual methods.
4. Reduced errors and downtime
Human error is one of the biggest risks in manual patching. Automation follows set rules and policies, ensuring updates are applied correctly. Scheduled deployments also minimize disruption to business operations.
Building an Automated Patch Management Strategy
Creating an effective automated patch management strategy involves several key components.
1. Asset discovery and inventory
The first step is knowing what devices and systems exist in the environment. Automated tools can scan the network and build a complete inventory, ensuring no system is overlooked.
2. Patch prioritization
Not all patches carry the same level of risk. Automation allows you to prioritize patches based on severity, so critical updates are deployed immediately while less urgent ones can wait.
3. Scheduling and deployment
Automated patching tools can schedule updates during off-hours or maintenance windows, reducing the impact on productivity. Staggered deployments can also be used to minimize the risk of widespread issues.
4. Monitoring and reporting
A strong strategy includes visibility into which patches were applied successfully and which failed. Automated systems provide detailed reports that help with compliance audits and internal reviews.
Bringing It All Together
Automating windows patch management in a hybrid environment is not just about convenience. It is about creating a secure, efficient, and consistent process that protects the organization from cyber threats while meeting compliance requirements.
Hybrid setups are complex by nature, but with the right automation strategy, IT teams can simplify patching, reduce risks, and ensure that all systems remain up to date.
The reality is that manual patch management cannot keep up with the pace of today’s IT world. With cyberattacks becoming more frequent and regulations becoming stricter, automation is the only way forward.
By investing in automated patch management, organizations can not only strengthen their security posture but also give their IT teams the freedom to focus on innovation and growth rather than repetitive tasks.