In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, with the increasing time the number of assets in an organization also keep on increasing.
Thus, maintaining an effective IT asset management (ITAM) system for the increased assets has become more critical than ever.
For asset managers, building an audit-ready ITAM strategy is not just about license compliance—it’s about ensuring the accuracy, security, and efficiency of an organization’s IT resources.
An audit-ready ITAM strategy helps avoid costly mistakes, reduces risks, and demonstrates a commitment to regulatory compliance and operational excellence.
In this blog, we’ll explore the essential steps and strategies to develop an ITAM system that stands up to scrutiny, ensuring that your assets are well-managed, documented, and ready for any audit.
From understanding the nuances of IT asset management audits to leveraging the right tools and techniques, this guide will provide the insights needed to build a robust and audit-ready ITAM strategy.
Understanding IT Asset Audits
What are the types of IT Asset Audits?
IT asset audits fall into two main categories: internal and external. Internal audits are performed by an organization’s own staff or dedicated audit team.
Their primary focus is to review and ensure that internal processes and procedures for managing IT assets are being adhered to.
This includes verifying that asset data are accurate, up-to-date, and reflective of the actual IT infrastructure.
Internal audits help identify gaps in compliance and operational efficiency before they become issues.
External audits are conducted by independent third-party firms or regulatory bodies.
These audits aim to validate the organization’s adherence to industry standards, regulatory requirements, and contractual obligations.
External audits provide an unbiased assessment of the IT asset management practices and offer credibility to stakeholders that the organization is meeting all necessary compliance requirements.
Now, if you ask which one is better? Then let me tell you that both types of audits are essential.
Both are required for maintaining robust IT asset management and ensuring transparency and accountability.
Objectives and Benefits
How can understanding the objectives and benefits of IT asset audits enhance your asset management practices?
For asset managers, grasping these aspects is crucial for developing an audit-ready IT asset management (ITAM) strategy.
By focusing on these goals, organizations not only improve their readiness for audits but also realize significant advantages in asset management.
This section will explore the primary objectives of conducting IT asset audits and the positive outcomes that come from achieving these goals.
Objectives:
1. Verify Accuracy:
One of the key objectives of IT asset audit is to verify the accuracy of asset records.
This involves validating that every asset—whether hardware or software—is properly cataloged with accurate details like location, ownership, status, and usage.
By cross-referencing records with physical or digital assets, organizations can identify discrepancies or outdated information.
Ensuring asset records are accurate is vital for tracking lifecycle stages, forecasting upgrades, and making strategic decisions.
Inaccurate data can lead to inefficient resource management, misallocated budgets, or vulnerabilities in security and regulation efforts.
2. Ensure Compliance:
Ensuring adherence to regulations is a pivotal goal of IT asset audits, which assists organizations in meeting legal, regulatory, and contractual obligations.
These audits evaluate whether licensing agreements, data protection laws, and industry-specific standards are being followed, thereby reducing the risk of fines or legal issues.
Maintaining conformity with these standards involves ongoing tracking of software licenses, monitoring usage limits, and staying updated on changing regulations.
Audits uncover any areas of non-compliance, allowing for prompt corrections.
Meeting these standards not only avoids financial penalties but also enhances organizational reputation and builds trust with customers and stakeholders.
3. Identify Improvements:
IT asset audits provide an opportunity to identify areas for improvement in the organization’s asset management practices.
These audits highlight inefficiencies, such as underutilized assets, redundant tools, or areas where processes can be streamlined.
By reviewing audit findings, organizations can develop strategies to optimize asset usage, reduce operational costs, and improve overall IT governance.
Regular audits also reveal potential security risks or mismanagement issues that, if addressed proactively, can enhance the organization’s operational effectiveness.
Identifying and implementing these improvements fosters continuous growth, driving both short-term efficiencies and long-term sustainability in asset management strategies.
Benefits:
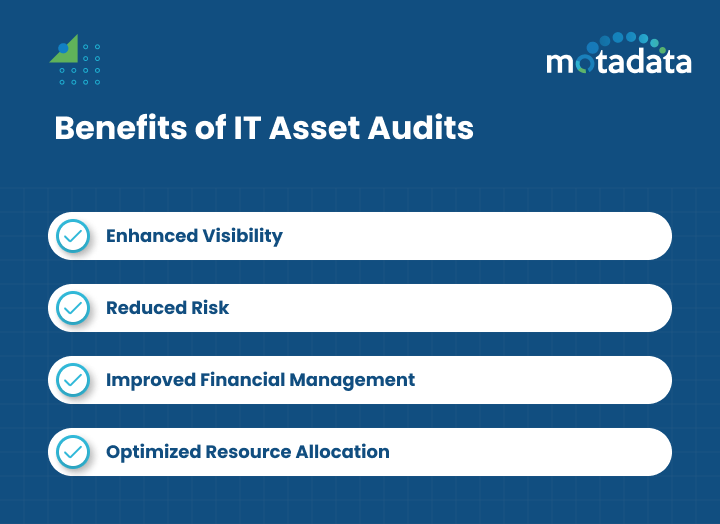
1. Enhanced Visibility:
By gaining comprehensive insights into asset utilization, organizations can better track the lifecycle of each asset, from acquisition to retirement.
This level of visibility allows IT managers to assess the performance, location, and status of hardware and software assets in real-time, leading to more informed decision-making.
With detailed reports and analytics, asset managers can proactively address issues like underutilization or misallocation, ultimately improving the overall efficiency and accuracy of IT asset management (ITAM) processes.
2. Reduced Risk:
Conducting regular IT asset audits helps significantly reduce risks related to non-compliance with licensing agreements, industry standards, and legal requirements.
Non-compliance can lead to costly fines, legal disputes, and reputational damage.
By ensuring that software licenses are up-to-date, and that assets adhere to regulatory standards, organizations can avoid such penalties.
Audits also help in identifying unauthorized or unmanaged assets that may pose security risks.
By mitigating these risks early on, organizations safeguard themselves from future liabilities and ensure continuous compliance with internal and external regulations.
3. Improved Financial Management:
IT asset audits offer an excellent opportunity for improved financial management by identifying cost-saving opportunities.
Regular audits reveal unused or underutilized assets, enabling organizations to reallocate resources, retire unnecessary assets, or avoid purchasing duplicate licenses.
Additionally, tracking software licenses ensures that companies only pay for what they use, avoiding unnecessary expenditures on excess licenses.
This optimized management of assets not only reduces cost of IT operations but also frees up the budget for strategic investments in new technology or upgrades, leading to more efficient use of financial resources.
Read Also: Top Benefits of Regular IT Asset Audits
4. Optimized Resource Allocation:
Audits highlight underutilized or redundant assets, making it easier to optimize resource allocation.
When assets are not being used efficiently, they waste valuable IT resources and budget.
By identifying these inefficiencies, organizations can strategically plan their asset deployment, ensuring that resources are allocated where they are needed most.
This allows for better budgeting, more efficient procurement processes, and a higher return on investment.
Optimized resource allocation also improves productivity by ensuring that employees have the necessary tools and technology at their disposal, while reducing the maintenance burden on IT teams.
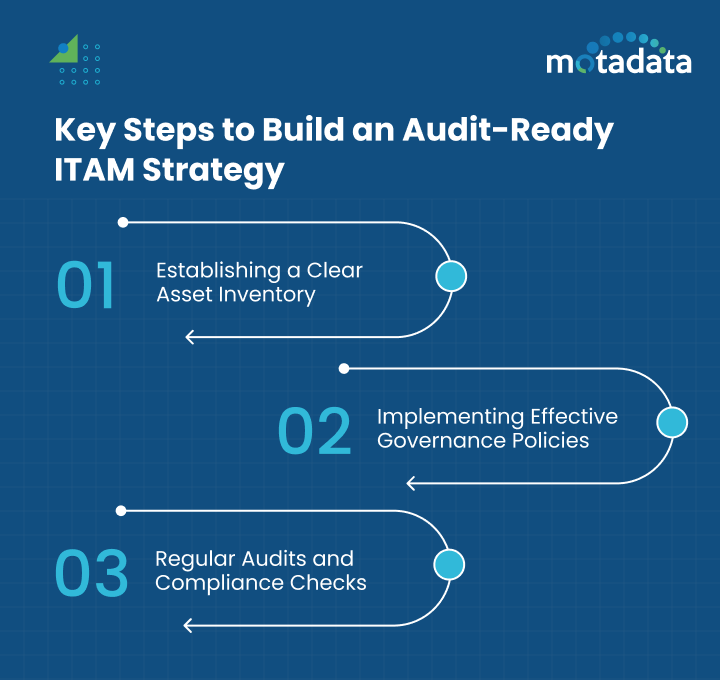
Key Steps to Build an Audit-Ready ITAM Strategy
To develop a robust IT asset management strategy that can withstand any audit, it’s essential to follow key steps.
These steps ensure that all aspects of managing your technology assets are well-organized and fully compliant with regulations.
1. Establishing a Clear Asset Inventory
A complete and accurate asset inventory is the cornerstone of an audit-ready ITAM strategy.
This involves creating and maintaining a detailed record of all IT assets, including hardware, software, and cloud resources.
Regular updates to the inventory, including adding new assets and removing obsolete ones, are essential to ensure accuracy and completeness.
2. Implementing Effective Governance Policies
Effective governance policies provide a framework for managing IT assets and ensuring compliance with regulations.
This includes establishing clear procedures for asset acquisition, usage, maintenance, and disposal.
Governance policies should also define roles and responsibilities, outline compliance requirements, and set guidelines for regular reviews and updates.
3. Regular Audits and Compliance Checks
Conducting regular internal audits and compliance checks helps ensure that the ITAM system remains aligned with organizational policies and external regulations.
These audits should be scheduled at regular intervals and include a thorough review of asset records, usage patterns, and compliance with licensing agreements.
Tools and Techniques for ITAM Audit Readiness
Preparing for IT asset audits requires more than just maintaining accurate records.
To ensure an audit-ready IT asset management (ITAM) strategy, organizations must prepare an audit checklist of which the main point is to leverage the right tools and techniques that streamline processes and enhance visibility.
By utilizing specialized ITAM software and incorporating advanced reporting methods, businesses can automate asset tracking, ensure compliance, and present data in a clear, audit-friendly format.
These tools not only simplify asset management but also help prevent discrepancies and ensure readiness for any audit scenario.
Recommended ITAM Software and Tools
Implementing the right ITAM software is vital for ensuring audit readiness.
Solutions like Motadata ServiceOps offer comprehensive tools to automate various IT asset management processes.
These tools provide features such as automated asset discovery, real-time tracking of asset lifecycles, and detailed reporting capabilities.
By using these tools, organizations can maintain accurate asset records, streamline the process of ensuring compliance, and be prepared for both internal and external audits.
Automation also minimizes human error, ensuring that audits are smoother and more efficient.
Data Visualization and Reporting Techniques
Clear and effective data presentation is a key part of audit readiness.
Data visualization tools such as interactive dashboards and customized reports help asset managers display critical information like asset utilization, compliance status, and ownership at a glance.
These visual aids make it easier to identify discrepancies and track real-time changes.
Additionally, techniques such as trend analysis, historical comparisons, and exception reporting provide valuable insights into asset performance and compliance trends, helping organizations address potential audit concerns proactively.
Common Challenges and Solutions
When preparing an IT asset management (ITAM) strategy for audits, organizations often face several common challenges that can complicate the process.
These challenges, such as maintaining accurate asset records and managing shadow IT, can lead to compliance risks and inefficiencies.
However, understanding these hurdles is the first step toward overcoming them.
By implementing effective solutions like automated tools, proactive monitoring, and regular internal audits, organizations can not only mitigate these risks but also ensure they are audit-ready at all times.
In this section, we explore some of the most common ITAM challenges and practical solutions to address them.
Addressing Common ITAM Challenges
1. Maintaining Accurate Asset Records:
Keeping an accurate and up-to-date inventory of IT assets is a persistent challenge, particularly in large organizations with devices spread across multiple locations.
Inaccuracies in asset records, such as outdated information or untracked assets, can lead to significant gaps in asset management.
These gaps not only hinder effective asset tracking but also heighten the risk of non-compliance during audits.
To overcome this challenge, organizations should implement automated asset discovery tools and establish robust procedures for regularly updating asset information to ensure records remain accurate and reliable.
2. Managing Shadow IT:
Shadow IT—unauthorized devices or software applications used within an organization—presents a major challenge for IT asset management.
These unregistered assets often bypass formal approval processes, making them difficult to track and manage.
This lack of visibility can complicate compliance efforts, increase security risks, and create significant hurdles during audits.
To address shadow IT, organizations should enforce strict policies on device and software approvals, implement comprehensive monitoring solutions, and encourage employees to report any unauthorized technology to the IT department for proper management.
3. Ensuring Compliance with Licensing Agreements:
Navigating the complexities of software licensing agreements is a common struggle for many organizations.
With diverse vendors and various licensing models, maintaining compliance can be challenging.
Mismanagement of licenses, such as failing to track usage or missing renewal dates, can lead to legal penalties, financial losses, and failed audits.
To ensure compliance, organizations should establish clear procedures for managing software licenses, utilize automated tools for tracking and renewing licenses, and regularly review licensing terms to align with usage and contractual obligations.
Solutions to Ensure Audit Readiness
1. Regular Audits and Monitoring:
Conducting regular internal audits is essential for maintaining the accuracy and currency of asset records.
Frequent audits help identify and rectify discrepancies promptly, reducing the risk of non-compliance during official reviews.
Coupled with proactive monitoring, these ITAM practices allow organizations to stay ahead of potential issues by quickly addressing any irregularities or gaps in asset management before they escalate into compliance problems.
2. Utilizing Automated Discovery Tools:
Automated discovery tools play a crucial role in managing and monitoring IT assets by continuously scanning networks to identify connected devices and software.
These tools facilitate the detection and management of shadow IT, providing comprehensive visibility into all assets within the organization.
By automating asset discovery, organizations can reduce security threats, streamline asset tracking, and enhance their preparedness for audits, ensuring that all assets are accounted for and properly managed.
3. Comprehensive Documentation and Compliance Reviews:
Maintaining thorough and up-to-date documentation is vital for audit readiness.
This includes detailed records of asset inventories, licensing agreements, hardware specifications, and software usage.
Regular compliance reviews of this documentation ensure that all assets and their management practices align with legal and contractual obligations.
By systematically reviewing and updating documentation, organizations can mitigate risks associated with non-compliance and ensure they meet all regulatory and contractual requirements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, creating an audit-ready ITAM strategy requires a systematic approach that blends precise asset tracking, robust governance policies, and the implementation of specialized ITAM tools.
Establishing a comprehensive asset inventory, enforcing clear governance measures, and utilizing advanced software like Motadata ServiceOps are key to ensuring continuous compliance.
By adopting these best practices, organizations can streamline their IT asset audits, reduce the risks of non-compliance, and enhance operational efficiency.
Moreover, this proactive approach not only strengthens audit readiness but also improves overall security, resource optimization, cost optimization, and long-term IT asset management success.
FAQs:
An audit-ready ITAM strategy ensures IT assets are accurately tracked, compliant with regulations, and prepared for audits.
It involves maintaining up-to-date records, implementing governance policies, and using tools to streamline reporting and compliance checks.
The key components of an audit-ready ITAM strategy include:
- Accurate Asset Inventory: Maintaining a detailed and up-to-date record of all IT assets.
- Governance Policies: Implementing clear policies for managing assets and ensuring compliance.
- Regular Audits: Conducting periodic internal audits to verify asset records and detect discrepancies.
- Automated Tools: Utilizing ITAM software for asset tracking, reporting, and compliance checks.
- Comprehensive Documentation: Keeping detailed records of licensing agreements, software usage, and hardware specifications.
To minimize blind spots in your IT asset inventory:
- Use Automated Discovery Tools: These continuously scan networks to identify all connected devices and software.
- Conduct Regular Audits: Periodic internal audits help ensure that your inventory stays accurate and complete.
- Track Shadow IT: Implement policies to monitor and control unauthorized devices or software.
- Centralize Asset Management: Maintain all asset data in a single, unified ITAM system for better visibility and tracking.
- Engage Employees: Encourage staff to report unregistered devices or software.
ITAM tools play a crucial role in developing an audit-ready strategy by:
- Automating Asset Discovery: They continuously track and record all IT assets across the organization, ensuring accurate inventory management.
- Streamlining Compliance Monitoring: ITAM tools help monitor license usage, contractual obligations, and regulatory requirements in real time.
- Facilitating Reporting: They generate detailed reports on asset lifecycles, usage, and compliance status, making audit preparation smoother.
- Reducing Human Error: By automating processes, ITAM tools reduce the risk of mistakes in asset tracking and documentation.