As per a Gartner study, the average cost of downtime per minute is $5600. This shows the critical financial impact of the system and interrupted service availability.
Thus, preventing and reducing downtime becomes imperative to ensure operational efficiency.
To prevent downtime, enterprises must measure and track their service delivery performance in today’s fast-moving digital world.
Incident management solution can measure various metrics and monitor the uptime and downtime of the systems.
Even a tiny glitch can disrupt the operations, costing the enterprises a considerable deal of money.
Incident metrics are an excellent way to understand how, when, and why some incidents occur and how enterprises can avoid them.
This blog post will explore various incident management metrics in detail, but before that, let us cover some basics first.
What is Incident Management

Incident management is a structured approach to identifying, responding, and resolving incidents within an enterprise’s IT infrastructure, services, or operations.
The sole purpose of incident management is to restore services rapidly, reduce the negative user experience, and prevent future disruptions.
It consists of tools and processes that minimize the impact of incidents on business operations, ensuring smooth business operations.
Importance of Incident Management Metrics:
Incident management metrics are integral to ensure efficiency in how enterprises respond to incidents.
Enterprises can rapidly address problems, meet service level agreements, and allocate resources properly by tracking incident management metrics, thus reinforcing operational efficiency, reliability, and resilience.
MTTR, MTBF, MTTF, and MTTA are abbreviations of some of the most crucial incident management metrics.
In the domain of IT service management, these acronyms help organizations plan their resources to ensure they can take care of problems caused by failed hardware and software glitches.
The full forms are as follows:
- Mean Time to Repair
- Mean Time Between Failure
- Mean Time to Failure
- Mean Time to Acknowledge
Let’s take a deep dive into each metric.
What is Mean Time to Repair (MTTR)?
Mean time to repair (MTTR) is the average amount of time required to repair a system and reinstate it to full functionality.
The MTTR calculation begins once a repair starts and continues until the disrupted services are completely restored, including any testing time needed.
In the IT service management industry, the R in MTTR doesn’t always symbolize repair. It could also represent recovery, response, or resolve.
While all these metrics correspond, they have their own implications, so it is always a good practice to clarify which MTTR is to be used.
Let’s briefly look at what each of them means.
Mean time to recovery (MTTR) is the average time it takes to recover from a breakdown of a device or system.
This spans the entire process from shutdown due to an outage to the time the system is completely operational again.
MTTR is a good indicator to measure the speed of the overall recovery process.
Mean time to respond (MTTR) stands for the average time it takes to recover from a system failure from when the first failure alert came in, not including any delay in the alert system.
This MTTR is typically used in cybersecurity to measure the team’s efficiency in defusing system attacks.
Mean time to resolve (MTTR) represents the average time spent to completely resolve a system breakdown including the time it takes to detect the failure, diagnose the issue, and resolve the issue by ensuring the breakdown doesn’t happen again.
This MTTR metric is mostly used for measuring the resolution process of unforeseen incidents and not service requests.
How do you calculate MTTR?
Since MTTR is an incident management metric that IT teams utilize to keep repairs on track, businesses should aim to keep the MTTR number as low as possible.
This is achievable by improving the productivity of the repair processes’ teams. MTTR can be calculated as follows,
MTTR= total time spent on repairs during a given period/number of repairs
Let’s assume there were 6 failures in a system, and the maintenance required to restore the system to full functionality took 3 hours, which is 180 minutes. So, the MTTR would be,
MTTR=180 / 6= 30 mins
This means that an organization’s MTTR is 30 minutes, which is the time on average the organization spends on each downtime.
Drive digital transformation with Motadata’s AI-enabled service desk that helps reduce MTTR around 80%– Want to know more?
Contact our expert sales team at sales@motadata.com or Try 30 free trial today.
Limitations of MTTR
- MTTR only evaluates the incident’s time taken to repair without considering its severity or user impact.
- Less reliable for complex incidents.
- It does not count the time from the occurrence of incidence to detection.
- It does not factor in ways to prevent incidents proactively.
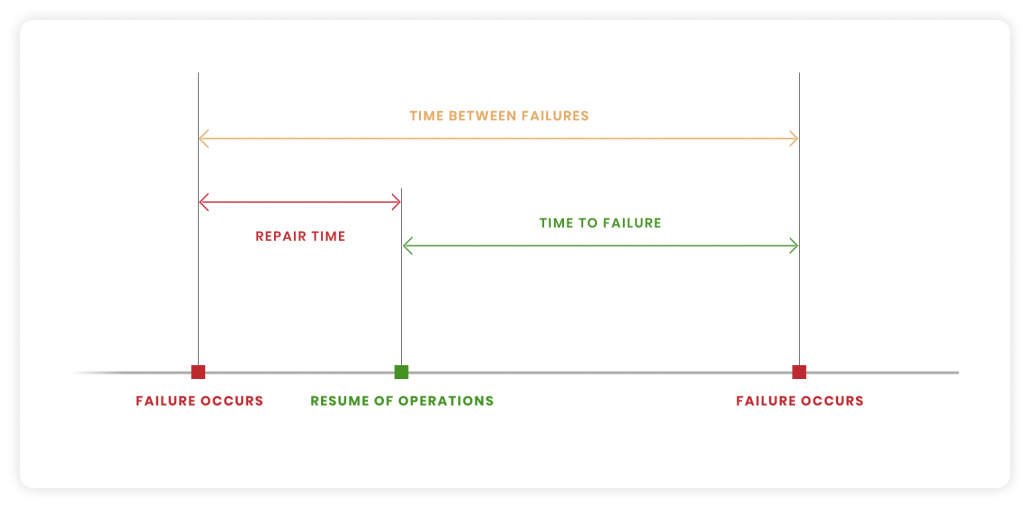
What is Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF)?
Mean time between failures (MTBF) is the average time passed between a repairable failure of a hardware and the next time it occurs.
MTBF gauges availability and reliability, so the higher the number of MTBF, the more reliable the system.
MTBF is a metric that aims to help customers make informed decisions about when to upgrade a system or put hardware into maintenance.
If, after a preventive maintenance phase, the MTBF has improved, this suggests an improvement in the reliability of the hardware. The rise in MTBF also demonstrates the efficiency of the maintenance processes.
How do you calculate MTBF?
MTBF is the time passed between one failure to the next. Mathematically, it can be calculated as follows,
MTBF=total operational uptime between failures / total number of failures
Suppose a system functions perfectly for 13 hours. During this period, 3 failures occurred, which caused a total downtime of 1 hour. So, the MTBF would be,
MTBF = (13-1) / 3 = 4 hours
This figure means that a failure in the system occurs every 4 hours, causing the system to be down and generating losses for the organization.
Tracking this metric can help plan strategies that can reduce this downtime.
Since MTBF is used to track reliability, it only reflects unexpected outages and does not consider any probable downtime during planned maintenance.
As we mentioned earlier, MTBF is used to track failures in repairable systems. A metric called Mean Time to Failure (MTTF) tracks failures that require a system replacement.
Limitations of MTBF:
- MTBF provides no information on the cause or severity of the failure
- Tracking failure metrics becomes difficult as asset’s life and breakdowns increase
- The reliability of MTBF may significantly vary because of manufacturing defects, human errors, etc.
What is Mean Time To Failure (MTTF)?
Mean time to failure (MTTF) is the average time passed between non-repairable hardware failures.
MTTF measures the reliability of non-repairable systems and signifies the extent of time that the system is expected to function before it fails completely.
MTTF is an important metric used to measure the lifespan of replaceable or non-repairable hardware like keyboards, batteries, desk telephones, mice, etc.
Historical data on the MTTF of each kind of hardware allows IT technicians to plan obsolescence in a phased manner.
Since the metric is used to identify how long a system would usually last, seeing whether a new version is outdoing the old would also help understand expected lifetimes and when to plan system check-ups.
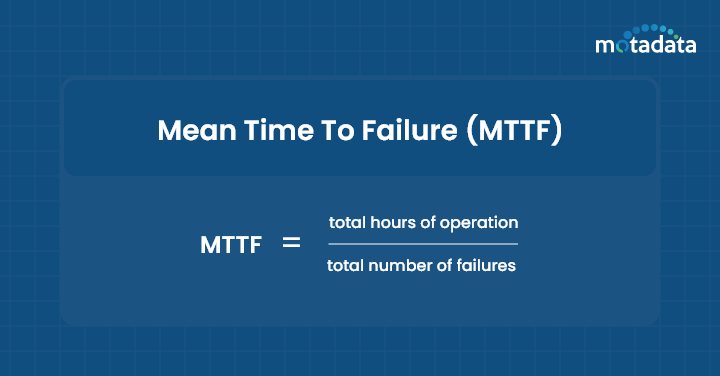
How do you calculate MTTF?
MTTF is the primary indicator of non-repairable hardware’s reliability, so the intention is to amplify the asset lifetime.
Shorter MTTF leads to frequent downtime and disruptions. To calculate MTTF, use the below formula,
MTTF=total hours of operation / total number of failures
Assuming we were to examine three identical systems until all of them failed. The first system lasted 14 hours, the second one lasted 16 hours, and the third lasted 12 hours. MTTF, in this instance, would be,
MTTF= (14 + 16 + 12) / 3 = 14 hours.
This means that this system, on average, would need to be replaced every 14 hours to prevent longer downtimes and subsequent damages.
Limitations of MTTF:
- MTTF falls short when it comes to measuring assets that last longer
- Assumes failures follow a predictable pattern
- No insights on how much time goes into repairing systems after failure
- It is not suitable for evaluating the reliability of complex systems with interdependent elements.
What is Mean Time To Acknowledge (MTTA)?
Mean time to acknowledge (MTTA) is the average time it takes for an organization to respond to complaints, outages, or incidents across all departments.
The incident management metric MTTA tracks a support team’s responsiveness and the alert system’s efficiency.
Sluggish responses can reduce the effectiveness of workers when internal systems face issues and cost organizations money.
Organizations can optimize their processes by tracking and minimizing MTTA, improving customer satisfaction, and enhancing profits.
How do you calculate MTTA?
MTTA is a valuable measure to monitor responsiveness. If a team is taking too long to respond and suffers from alert fatigue, this metric will help highlight the issue. To calculate MTTA, use the following mathematical representation,
MTTA=total time taken between alert and acknowledgment / total number of incidents
Let’s say 5 incidents happened in an organization, and it took a total of 30 minutes between alert and acknowledgment for all the incidents; then the MTTA would be
MTTA= 30 / 5 = 6 minutes
This means that the MTTA for the organization is 6 minutes, and the organization should work on reducing this time to optimize its resolution process.
Limitations of MTTA:
- MTTA only measures acknowledgment, ignoring resolution time and user satisfaction.
- It doesn’t consider the time to resolve issues, potentially leaving customers dissatisfied.
- Overemphasizing MTTA can lead to rushed acknowledgments, compromising quality.
- MTTA can vary widely based on the complexity of requests.
Conclusion
To summarize, mean time to repair (MTTR) is a measure through which you can see how fast you can get a failed hardware to work again.
Mean time between failures (MTBF) gives you a sense of how effective your support team is at minimizing or preventing impending incidents.
Using the metric mean time to failure (MTTF), you can determine a system’s or hardware’s lifespan.
Finally, mean time to acknowledge (MTTA) is a valuable measure through which you can track your IT support team’s responsiveness.
Now that you understand these incident metrics in detail, you will realize that each metric offers a different perspective.
When used simultaneously, these robust metrics can provide a deeper perspective on how your support team manages service disruptions and help you reduce losses due to inefficiencies and quality issues.
To learn more about which other service management metrics you should be tracking, read our article 7 Important Service Desk Metrics to Measure.
Get rid of problems caused by failed hardware and software glitches with Motadata’s unified ServiceOps IT Incident Management solution.
Improve ROI by reducing errors – Want to know more about our solutions? Contact us today.